CD19 CAR-T cell therapy: a new dawn for autoimmune rheumatic diseases?
- PMID: 39742256
- PMCID: PMC11685126
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1502712
CD19 CAR-T cell therapy: a new dawn for autoimmune rheumatic diseases?
Abstract
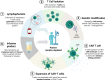
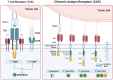
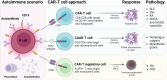
Autoimmune rheumatic diseases (ARDs), such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and systemic sclerosis, involve dysregulated immune responses causing chronic inflammation and tissue damage. Despite advancements in clinical management, many patients do not respond to current treatments, which often show limited efficacy due to the persistence of autoreactive B cells. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy, which has shown success in oncology for B cell malignancies, targets specific antigens and involves the adoptive transfer of genetically engineered T cells. CD19 CAR-T cells, in particular, have shown promise in depleting circulating B cells and achieving clinical remission. This review discusses the potential of CD19 CAR-T cells in ARDs, highlighting clinical achievements and addressing key considerations such as optimal target cell populations, CAR construct design, acceptable toxicities, and the potential for lasting immune reset, crucial for the safe and effective adoption of CAR-T cell therapy in autoimmune treatments.
Keywords: CD19 CAR-T; autoimmune rheumatic diseases; rheumatoid arthritis; systemic lupus erythematosus; systemic sclerosis.
Copyright © 2024 Rangel-Peláez, Martínez-Gutiérrez, Tristán-Manzano, Callejas, Ortego-Centeno, Martín and Martín.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors MT-M and FM were employed by the company Pfizer-University of Granada-Andalusian Regional Government Centre for Genomics and Oncological Research GENYO. The remaining authors declare that the review was written in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

