Determinants of increased muscle insulin sensitivity of exercise-trained versus sedentary normal weight and overweight individuals
- PMID: 39742483
- PMCID: PMC11691647
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adr8849
Determinants of increased muscle insulin sensitivity of exercise-trained versus sedentary normal weight and overweight individuals
Abstract
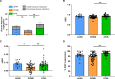
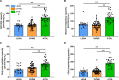
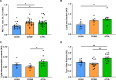
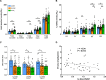
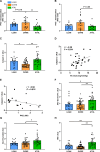
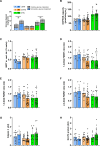
The athlete's paradox states that intramyocellular triglyceride accumulation associates with insulin resistance in sedentary but not in endurance-trained humans. Underlying mechanisms and the role of muscle lipid distribution and composition on glucose metabolism remain unclear. We compared highly trained athletes (ATHL) with sedentary normal weight (LEAN) and overweight-to-obese (OVWE) male and female individuals. This observational study found that ATHL show higher insulin sensitivity, muscle mitochondrial content, and capacity, but lower activation of novel protein kinase C (nPKC) isoforms, despite higher diacylglycerol concentrations. Notably, sedentary but insulin sensitive OVWE feature lower plasma membrane-to-mitochondria sn-1,2-diacylglycerol ratios. In ATHL, calpain-2, which cleaves nPKC, negatively associates with PKCε activation and positively with insulin sensitivity along with higher GLUT4 and hexokinase II content. These findings contribute to explaining the athletes' paradox by demonstrating lower nPKC activation, increased calpain, and mitochondrial partitioning of bioactive diacylglycerols, the latter further identifying an obesity subtype with increased insulin sensitivity (NCT03314714).
Figures
References
-
- Krssak M., Falk Petersen K., Dresner A., DiPietro L., Vogel S. M., Rothman D. L., Roden M., Shulman G. I., Intramyocellular lipid concentrations are correlated with insulin sensitivity in humans: A 1H NMR spectroscopy study. Diabetologia 42, 113–116 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Levin K., Daa Schroeder H., Alford F. P., Beck-Nielsen H., Morphometric documentation of abnormal intramyocellular fat storage and reduced glycogen in obese patients with type II diabetes. Diabetologia 44, 824–833 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Perseghin G., Lattuada G., De Cobelli F., Ragogna F., Ntali G., Esposito A., Belloni E., Canu T., Terruzzi I., Scifo P., Del Maschio A., Luzi L., Habitual physical activity is associated with intrahepatic fat content in humans. Diabetes Care 30, 683–688 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Goodpaster B. H., He J., Watkins S., Kelley D. E., Skeletal muscle lipid content and insulin resistance: Evidence for a paradox in endurance-trained athletes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 5755–5761 (2001). - PubMed

