Day 3 neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and its derived indices predict 90-day poor outcomes following mechanical thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke patients
- PMID: 39744114
- PMCID: PMC11688358
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1496628
Day 3 neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and its derived indices predict 90-day poor outcomes following mechanical thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke patients
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the dynamic changes in neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and its derived indices following mechanical thrombectomy (MT) in patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) and evaluate their predictive value for prognosis.
Methods: This single-center retrospective cohort study included AIS patients who underwent MT at Zhongshan Hospital of Xiamen University from January 2018 to February 2024. Peripheral blood samples were collected on admission, day 1, and day 3 after MT to determine the NLR, derived NLR (dNLR), and neutrophil-monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio (NMLR). The primary endpoint was poor functional outcome at 90 days (modified Rankin scale score 3-6). The secondary endpoints included post-operative hemorrhagic transformation, malignant cerebral edema, in-hospital mortality, and 90-day all-cause mortality. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to evaluate predictive performance, and multivariate logistic regression models were employed to explore the independent associations between inflammatory markers and prognosis.
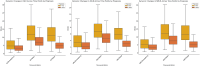
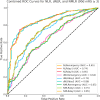
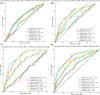
Results: A total of 423 eligible patients were included. Both groups showed similar dynamic trends in inflammatory markers, peaking on day 1 post-MT and subsequently declining. However, the poor outcome group (n = 255, 60.28%) maintained higher levels on day 3, whereas the good outcome group showed a significant decreasing trend. ROC curve analysis revealed that the NLR (AUC = 0.85, 95% CI: 0.81-0.89), dNLR (AUC = 0.86, 95% CI: 0.82-0.89), and NMLR (AUC = 0.85, 95% CI: 0.81-0.89) on day 3 post-MT had the strongest predictive power for 90-day poor outcomes. After comprehensive adjustment for confounders, these inflammatory markers were independently associated with 90-day poor outcomes: for each unit increase in the NLR, the risk of poor outcome increased by 38% (OR = 1.38, 95% CI: 1.28-1.49, p < 0.001); for dNLR, it increased by 104% (OR = 2.04, 95% CI: 1.73-2.40, p < 0.001); and for NMLR, it increased by 35% (OR = 1.35, 95% CI: 1.26-1.45, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Inflammatory markers (NLR, dNLR, and NMLR) on day 3 post-MT can serve as independent predictors of prognosis in AIS patients treated with MT. Dynamic monitoring of inflammatory markers may facilitate early risk stratification and guide individualized treatment strategies.
Keywords: acute ischemic stroke; derived neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; inflammatory markers; mechanical thrombectomy; neutrophil-monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; prognosis.
Copyright © 2024 Gao, Annadurdyyev, Yu, Huang, Liu, Lin, Li and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel peripheral blood cell ratios: Effective 3-month post-mechanical thrombectomy prognostic biomarkers for acute ischemic stroke patients.J Clin Neurosci. 2021 Jul;89:56-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2021.04.013. Epub 2021 May 5. J Clin Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34119295
-
Day 1 neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) predicts stroke outcome after intravenous thrombolysis and mechanical thrombectomy.Front Neurol. 2022 Aug 9;13:941251. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.941251. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36016545 Free PMC article.
-
High Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio and Low Lymphocyte-Monocyte Ratio Combination after Thrombolysis Is a Potential Predictor of Poor Functional Outcome of Acute Ischemic Stroke.J Pers Med. 2022 Jul 27;12(8):1221. doi: 10.3390/jpm12081221. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35893315 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of inflammatory markers NLR, PLR, LMR, dNLR, ANC in melanoma patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a meta-analysis and systematic review.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 18;15:1482746. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1482746. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39493767 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in acute ischemic stroke patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Neurol. 2021 May 11;21(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12883-021-02222-8. BMC Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33975565 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Distinct trajectory patterns of neutrophil-to-albumin ratio predict clinical outcomes after endovascular therapy in large vessel occlusion stroke.Front Aging Neurosci. 2025 Jun 4;17:1570662. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1570662. eCollection 2025. Front Aging Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40535510 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lakomkin N, Dhamoon M, Carroll K, Singh IP, Tuhrim S, Lee J, et al. . Prevalence of large vessel occlusion in patients presenting with acute ischemic stroke: a 10-year systematic review of the literature. J Neurointerv Surg. (2019) 11:241–5. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2018-014239, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker K, et al. . Guidelines for the early Management of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. (2019) 50:e344–418. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000211, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

