Metabolic reprogramming in lung cancer and its clinical implication
- PMID: 39744129
- PMCID: PMC11688361
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1516650
Metabolic reprogramming in lung cancer and its clinical implication
Abstract
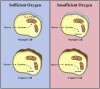
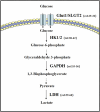
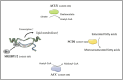
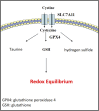
Lung cancer has posed a significant challenge to global health, and related study has been a hot topic in oncology. This article focuses on metabolic reprogramming of lung cancer cells, a process to adapt to energy demands and biosynthetic needs, supporting the proliferation and development of tumor cells. In this study, the latest studies on lung cancer tumor metabolism were reviewed, including the impact of metabolic products and metabolic enzymes on the occurrence and development of lung cancer, as well as the progress in the field of lung cancer treatment targeting relevant metabolic pathways. This provides some promising potential directions into exploring lung cancer tumor metabolism and helps researchers to better understand lung cancer.
Keywords: amino acid metabolism; glucose; lipid metabolism; lung cancer; metabolic reprogramming.
Copyright © 2024 Huang, Fan, Gong, Ren, Chen and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ao Y.-Q., Gao J., Zhang L.-X., Deng J., Wang S., Lin M., et al. (2023). Tumor-infiltrating CD36+CD8+T cells determine exhausted tumor microenvironment and correlate with inferior response to chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 23, 367. 10.1186/s12885-023-10836-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

