Novel automated method to assess group dynamics reveals deficits in behavioral contagion in rats with social deficits
- PMID: 39744143
- PMCID: PMC11688315
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2024.1519486
Novel automated method to assess group dynamics reveals deficits in behavioral contagion in rats with social deficits
Abstract
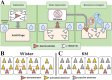
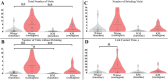
Behavioral copying is a key process in group actions, but it is challenging for individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). We investigated behavioral contagion, or instinctual replication of behaviors, in Krushinky-Molodkina (KM) rats (n = 16), a new potential rodent model for ASD, compared to control Wistar rats (n = 15). A randomly chosen healthy Wistar male ("demonstrator rat") was introduced to the homecage of experimental rats ("observers") 10-14 days before the experiments to become a member of the group. For the implementation of the behavioral contagion experiment, we used the IntelliCage system, where rats can live in a group of 5-6 rats and their water visits can be automatically scored. During the experiment, the demonstrator was taken out of IntelliCage for a pre-test water deprivation and then placed back for the behavioral contagion test. As a result, a drinking behavior of the water-deprived demonstrator rat prompted water-seeking and drinking behaviors in the whole group. Unlike the Wistar controls, KM observers showed fewer visits to the drinking bottles, particularly lacking inspection visits (i.e., visits without drinking). The control group, in contrast, exhibited a dynamic, cascade-like visiting of the water corners. The proportion of activated observers in KM rats was significantly lower, as compared to Wistar ones, and they did not mimic other observer rats. KM rats, therefore, displayed an attenuated pattern of behavioral contagion, highlighting social deficits in this strain. This study suggests that measuring group dynamics of behavioral contagion in an automated, non-invasive setup offers valuable insights into social behavior in rodents.
Keywords: IntelliCage; autism spectrum disorder; automated behavioral testing; behavioral contagion; group behavior; rat; social deficit.
Copyright © 2024 Smirnov, Starkov, Sysoeva and Midzyanovskaya.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Early evidence for emotional play contagion in juvenile ravens.Anim Cogn. 2021 Jul;24(4):717-729. doi: 10.1007/s10071-020-01466-0. Epub 2021 Jan 9. Anim Cogn. 2021. PMID: 33420859 Free PMC article.
-
[Modification of the Rat Ethogram by Contagion Behavior].Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova. 2016 Jul;66(4):484-492. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova. 2016. PMID: 30695526 Russian.
-
When is emotional contagion adaptive?J Theor Biol. 2015 Sep 7;380:480-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2015.06.014. Epub 2015 Jun 23. J Theor Biol. 2015. PMID: 26113192
-
IntelliCage: the development and perspectives of a mouse- and user-friendly automated behavioral test system.Front Behav Neurosci. 2024 Jan 3;17:1270538. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2023.1270538. eCollection 2023. Front Behav Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38235003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Social contagion of pain and fear results in opposite social behaviors in rodents: meta- analysis of experimental studies.Front Behav Neurosci. 2024 Oct 29;18:1478456. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2024.1478456. eCollection 2024. Front Behav Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39534728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Birioukova L. M., Van Luijtelaar G., Midzyanovskaya I. S. (2024). D1-like and D2-like dopamine receptors in the rat prefrontal cortex: Impacts of genetic generalized epilepsies and social behavioral deficits. Receptors 3 36–57. 10.3390/receptors3010004 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

