Receptor-Interacting Protein Kinase 3-Mediated Modulation of Endothelial Cell Necroptosis and Mitochondrial Dysfunction through AMPK/Drp1 Signaling Pathway: Insights into the Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury
- PMID: 39744171
- PMCID: PMC11659830
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.104932
Receptor-Interacting Protein Kinase 3-Mediated Modulation of Endothelial Cell Necroptosis and Mitochondrial Dysfunction through AMPK/Drp1 Signaling Pathway: Insights into the Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury
Abstract
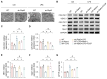
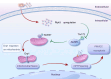
Receptor-interacting protein 3 (Ripk3) plays a crucial part in acute lung injury (ALI) by regulating inflammation-induced endothelial damage in the lung tissue. The precise mechanisms through which Ripk3 contributes to the endothelial injury in ALI still remain uncertain. In the current research, we employed Ripk3-deficient (Ripk3-/-) mice to examine the role of Ripk3 in ALI progression, focusing on its effects on endothelial cells (ECs), mitochondrial damage and necroptosis. Our study observed significant Ripk3 upregulation in lipopolysaccharide- (LPS-) treated lung tissues, as well as in murine pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (PMVECs). Ripk3 deletion improved lung tissue morphology, reduced inflammation, oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction under LPS challenge. It also mitigated LPS-induced necroptosis and mitochondrial damage in PMVECs. Ripk3 upregulation suppressed the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway and activated Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission, increasing mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) opening and PMVEC necroptosis. Conversely, Ripk3 deletion activated the AMPK/Drp1-mitochondrial fission pathway, preventing mPTP opening and PMVEC necroptosis in ALI. These findings demonstrated that Ripk3 promotes necroptosis through the AMPK/Drp1/mPTP opening pathway, identifying a potential therapeutic target for ALI treatment.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; Cell necroptosis; Mitochondrial damage; Ripk3.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures





References
-
- Liu M, Chen Y, Wang S, Zhou H, Feng D, Wei J. et al. α-Ketoglutarate Modulates Macrophage Polarization Through Regulation of PPARγ Transcription and mTORC1/p70S6K Pathway to Ameliorate ALI/ARDS. Shock. 2020;53:103–13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

