tRNA-derived small RNAs in disease immunity
- PMID: 39744232
- PMCID: PMC11667222
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.102650
tRNA-derived small RNAs in disease immunity
Abstract
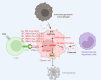
Recently, members of a unique species of non-coding RNA, known as transfer RNA-derived small RNAs (tsRNAs) have been reported to serve multiple molecular functions, including in cells that mediate immunity. Because of their low molecular weights, tsRNAs were previously difficult to detect and were thus overlooked, until now. In this review, we delve into the biogenesis of tsRNAs and their diverse biological functions, ranging from transcriptional regulation to modulation of mRNA translation. We highlight the current evidence demonstrating their involvement in the immune response, as well as how tsRNAs modulate immunity to influence tumor growth and spread, autoimmune disease pathology and infection by pathogens. We surmise that tsRNAs are likely informative as diagnostic markers of cellular homeostasis and disease, and that therapeutic targeting of tsRNAs could be beneficial for a range of human diseases. Improved knowledge on the functions for tsRNAs in the mammalian immune system will enable us to leverage tsRNAs for their effective clinical use as treatments for human health challenges.
Keywords: adaptive immunity; autoimmune diseases; biogenesis; non-coding RNA; tRNA-derived small RNA; tumor immunology.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



References
-
- Hoagland MB, Stephenson ML, Scott JF, Hecht LI, Zamecnik PC. A soluble ribonucleic acid intermediate in protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1958;231:241–57. - PubMed
-
- Muthukumar S, Li CT, Liu RJ, Bellodi C. Roles and regulation of tRNA-derived small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024;25:359–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

