Cervical Spinal Epidural Abscess From Haemophilus influenzae in an Adult: A Case Report
- PMID: 39744277
- PMCID: PMC11688608
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.74946
Cervical Spinal Epidural Abscess From Haemophilus influenzae in an Adult: A Case Report
Abstract
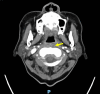
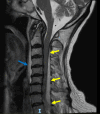
Pyogenic spinal infections due to Haemophilus influenzae (H. influenzae) are rare. After a search of the literature, we deemed our case to be the first description of spinal epidural abscess (SEA) from H. influenzae. This is a 74-year-old female patient with a history of diabetes who presented to the emergency department with fever and persistent paracervical pain after being initially diagnosed with viral sinusitis two days prior. The examination was negative for neurologic deficits. She was admitted for possible meningitis versus intramuscular abscess due to cerebrospinal fluid pleocytosis and CT imaging findings. However, an MRI obtained during the patient's admission revealed a multi-level cervical SEA, likely from an invasive H. influenzae infection, and the patient underwent evacuation surgery with a good outcome. Epidural abscesses are rarely present in isolation in the cervical region and can be mistaken for other more common infectious and non-infectious causes of neck pain on initial presentation and even as diagnostic work-up progresses. However, there is significant morbidity if diagnosis via advanced imaging and surgical treatment is delayed. We aim to present the first reported case of SEA from H. influenzae and increase awareness of this atypical presentation of a rare yet invasive disease.
Keywords: cervical pain; haemophilus influenzae; infectious disease; neck pain; neurologic emergency; pyogenic spinal infection; spinal epidural abscess.
Copyright © 2024, Qiao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Spontaneous epidural abscess: analysis of 15 cases with emphasis on diagnostic and prognostic factors. González-López JJ, Górgolas M, Muñiz J, López-Medrano F, Barnés PR, Fernández Guerrero ML. Eur J Intern Med. 2009;20:514–517. - PubMed
-
- Haemophilus species, a rare cause of vertebral osteomyelitis: case report and review of the literature. Brooks D, Zhou S, Kauffman C. Infect Dis Clin Pract. 2020;28:191–195.
-
- Spinal epidural abscess: contemporary trends in etiology, evaluation, and management. Rigamonti D, Liem L, Sampath P, et al. Surg Neurol. 1999;52:189–197. - PubMed
-
- Cervical spine epidural abscess in a patient with no predisposing risk factors. Vilke GM, Honingford EA. Ann Emerg Med. 1996;27:777–780. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
