Advanced Trauma Care With Tricalcium Phosphate Bone Grafts for Tibial Plateau Fractures: A Report of Three Cases
- PMID: 39744291
- PMCID: PMC11693410
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.74982
Advanced Trauma Care With Tricalcium Phosphate Bone Grafts for Tibial Plateau Fractures: A Report of Three Cases
Abstract
Advances in implants and biological therapies have significantly improved trauma care, offering surgeons a variety of solutions for complex cases. This study evaluates the outcomes of three patients with complex Schatzker type V tibial plateau fractures, treated with open reduction and internal fixation supplemented by tricalcium phosphate bone void filler. The surgical approach was selected based on the specific fracture pattern. Postoperative outcomes were assessed using the Oxford Knee Score (OKS), Visual Analog Scale (VAS) for pain, and EQ-5D-5L for quality of life. The results indicated high patient satisfaction (mean score of 8.67 ± 2.31) and low pain levels (mean VAS of 2.67 ± 2.31). The mean OKS was 32 (± 8.66), and the mean EQ-5D-5L VAS score was 88.33 (± 16.07). Follow-up assessments revealed a good to excellent range of motion, with no significant complications. No additional articular step-off was observed at follow-up. The study suggests that tricalcium phosphate bone grafts may be a promising biomaterial for enhancing recovery in complex tibial plateau fractures by providing mechanical support and promoting osteointegration.
Keywords: biocompatible materials; bone graft substitutes; open reduction and internal fixation (orif); tibial plateau fracture; tricalcium phosphate.
Copyright © 2024, Costa et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures


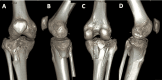

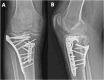
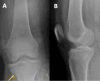
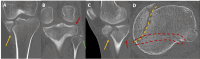
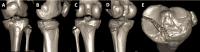
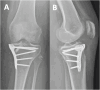

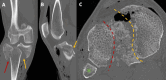



References
-
- Fracture healing: the diamond concept. Giannoudis P, Einhorn T, Marsh D. Injury. 2007;38:3–6. - PubMed
-
- Fracture nonunion in long bones: a literature review of risk factors and surgical management. Nicholson JA, Makaram N, Simpson A, Keating JF. Injury. 2021;52:0–11. - PubMed
-
- Failure of fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Ali AM, El-Shafie M, Willett KM. J Orthop Trauma. 2002;16:323–329. - PubMed
-
- Influence of bone quality on the strength of internal and external fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Ali AM, Saleh M, Eastell R, Wigderowitz CA, Rigby AS, Yang L. J Orthop Res. 2006;24:2080–2086. - PubMed
-
- Calcium phosphate cement augmentation in the treatment of depressed tibial plateau fractures with open reduction and internal fixation. Oztürkmen Y, Caniklioğlu M, Karamehmetoğlu M, Sükür E. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2010;44:262–269. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
