Heat acclimation mediates cellular protection via HSP70 stabilization of HIF-1α protein in extreme environments
- PMID: 39744422
- PMCID: PMC11667810
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.103122
Heat acclimation mediates cellular protection via HSP70 stabilization of HIF-1α protein in extreme environments
Abstract
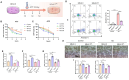
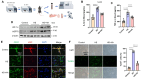
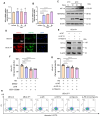
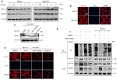
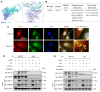
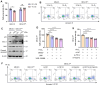
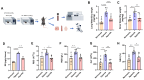
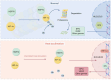
Heat acclimation (HA) is an evolutionarily conserved trait that enhances tolerance to novel stressors by inducing heat shock proteins (HSPs). However, the molecular mechanisms underlying this phenomenon remain elusive. In this study, we established a HA mouse model through intermittent heat stimulation. Subsequently, this model was evaluated using an array of physiological and histological assessments. In vitro, HA cell model with mouse brain microvascular endothelial cells (bEnd.3) was established and analyzed for cell viability and apoptosis markers. We investigated HA-mediated heat and hypoxia tolerance mechanisms using HIF-1α and HSP70 inhibitors and siRNA. Our results demonstrated that HA enhances the tolerance of bEnd.3 cells and mice to both heat and hypoxia, Mechanistically, HA upregulated the expression of HIF-1α and HSP70. However, inhibition of HIF-1α or HSP70 partially attenuated HA-induced tolerance to heat and hypoxia. Additionally, HA significantly decreased the ubiquitination levels of HIF-1α, whereas inhibition of HSP70 increased its ubiquitination. HA also substantially enhanced the interaction between HIF-1α and HSP70. In conclusion, our findings indicate that HA enhances tolerance to heat and hypoxia by stabilizing HIF-1α through increased interaction with HSP70. This discovery elucidates a novel mechanism of cellular protection conferred by HA and provides new strategies and potential targets for human adaptation to extreme environments.
Keywords: Heat acclimation; Heat shock protein 70; Heat stress; Hypoxia; Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha; Ubiquitination.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PI3K/Akt is required for heat shock proteins to protect hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha from pVHL-independent degradation.J Biol Chem. 2004 Apr 2;279(14):13506-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M310164200. Epub 2004 Jan 15. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14726529
-
Hsp70 and CHIP selectively mediate ubiquitination and degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha but Not HIF-2alpha.J Biol Chem. 2010 Feb 5;285(6):3651-3663. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.068577. Epub 2009 Nov 23. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 19940151 Free PMC article.
-
Ηypoxia-inducible factor-1α, von Hippel-Lindau protein, and heat shock protein expression in ophthalmic pterygium and normal conjunctiva.Mol Vis. 2014 Mar 30;20:441-57. eCollection 2014. Mol Vis. 2014. PMID: 24715760 Free PMC article.
-
Heat acclimation-mediated cross-tolerance in cardioprotection: do HSP70 and HIF-1alpha play a role?Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Feb;1188:199-206. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05101.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20201904 Review.
-
Heat acclimation-induced intracellular HSP70 in humans: a meta-analysis.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2020 Jan;25(1):35-45. doi: 10.1007/s12192-019-01059-y. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2020. PMID: 31823288 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Le Roy B, Martin-Krumm C, Pinol N, Dutheil F, Trousselard M. Human challenges to adaptation to extreme professional environments: A systematic review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2023;146:105054. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

