Quantitative Histopathology Analysis Based on Label-free Multiphoton Imaging for Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy Response Assessment
- PMID: 39744437
- PMCID: PMC11667811
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.102744
Quantitative Histopathology Analysis Based on Label-free Multiphoton Imaging for Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy Response Assessment
Abstract
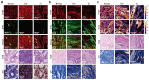
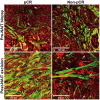
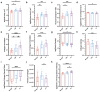
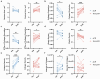
Accurate diagnosis and assessment of breast cancer treatment responses are critical challenges in clinical practice, influencing patient treatment strategies and ultimately long-term prognosis. Currently, diagnosing breast cancer and evaluating the efficacy of neoadjuvant immunotherapy (NAIT) primarily rely on pathological identification of tumor cell morphology, count, and arrangement. However, when tumors are small, the tumors and tumor beds are difficult to detect; relying solely on tumor cell identification may lead to false negatives. In this study, we used the label-free multiphoton microscopy (MPM) method to quantitatively analyze breast tissue at the cellular, extracellular, and textural levels, and identified 11 key factors that can effectively distinguish different types of breast diseases. Key factors and clinical data are used to train a two-stage machine learning automatic diagnosis model, MINT, to accurately diagnose breast cancer. The classification capability of MINT was validated in independent cohorts (stage 1 AUC = 0.92; stage 2 AUC = 1.00). Furthermore, we also found that some factors could predict and assess the efficacy of NAIT, demonstrating the potential of label-free MPM in breast cancer diagnosis and treatment. We envision that in the future, label-free MPM can be used to complement stromal and textural information in pathological tissue, benefiting breast cancer diagnosis and neoadjuvant therapy efficacy prediction, thereby assisting clinicians in formulating personalized treatment plans.
Keywords: breast cancer; extracellular matrix; label-free multiphoton imaging; neoadjuvant immunotherapy; quantitative analysis; texture.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Elston CW, Ellis IO. Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology. 1991;19:403–10. - PubMed
-
- Tan PH, Ellis I, Allison K, Brogi E, Fox SB, Lakhani S. et al. The 2019 World Health Organization classification of tumours of the breast. Histopathology. 2020;77:181–5. - PubMed
-
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Classification of Breast Tumours, 5th edn. Lyon: IARC Press. 2019.
-
- See SHC, Siziopikou KP. Pathologic evaluation of specimens after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: Current recommendations and challenges. Pathol Res Pract. 2022;230:153753. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

