Outcome of Preoperative Oral Steroids on Patients With Sinonasal Polyposis
- PMID: 39744450
- PMCID: PMC11685917
- DOI: 10.18787/jr.2024.00024
Outcome of Preoperative Oral Steroids on Patients With Sinonasal Polyposis
Abstract
Background and objectives: This study aimed to evaluate whether preoperative oral prednisolone improves the intraoperative parameters and postoperative outcomes over a 3-month period in patients of sinonasal polyposis who undergo functional endoscopic sinus surgery.
Methods: In a triple-blind, randomized controlled study, 43 patients diagnosed with sinonasal polyposis in the Department of ENT, AIIMS, Jodhpur, were enrolled. After obtaining institutional ethics clearance and registering the clinical trial, randomization was conducted to assign participants into experimental and control groups. Preoperatively, patients were assessed using the clinical severity score (Sino-nasal Outcome Test; SNOT-22), radiological severity score (Lund-Mackay score), and endoscopic severity scores (discharge-inflammation-polyp [DIP] score and Lund-Kennedy score). Intraoperative assessment was done using the Perioperative Sinus Endoscopy (POSE) score, the duration of surgery, intraoperative blood loss, and visual analog scale for visual field during surgery and for the ease of disease removal. Postoperatively, at 3 months all the preoperative parameters were reassessed, and, using independent t-test, comparison was made between the two groups.
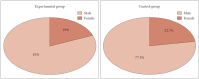
Results: Twenty-one patients were included in the experimental group (48%), and 22 in the control group (51%). Although the mean duration of surgery in the experimental group was shorter than in the control group, the difference was not statistically significant. Similarly, although the postoperative SNOT-22 score was lower in the experimental group compared to the control group, there was no statistically significant difference in outcomes between the two groups across any of the parameters assessed.
Conclusion: Although the role of oral steroids has been established in the treatment of sinonasal polyposis, our study did not find any significant difference between the group that received oral steroids prior to surgery and the group that received placebo.
Keywords: CRSwNP; Corticosteroids; Oral steroids; Sinonasal polyposis; Systemic steroids.
Copyright © 2024 by The Korean Rhinologic Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, Hellings PW, Kern R, Reitsma S, et al. Executive summary of EPOS 2020 including integrated care pathways. Rhinology. 2020;58(2):82–111. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya N. Assessing the additional disease burden of polyps in chronic rhinosinusitis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2009;118(3):185–9. - PubMed
-
- Stankiewicz J, Tami T, Truitt T, Atkins J, Winegar B, Cink P, et al. Impact of chronic rhinosinusitis on work productivity through one-year follow-up after balloon dilation of the ethmoid infundibulum. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2011;1(1):38–45. - PubMed
-
- Grayson JW, Hopkins C, Mori E, Senior B, Harvey RJ. Contemporary classification of chronic rhinosinusitis beyond polyps vs no polyps: a review. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020;146(9):831–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous