Prognostic Significance of CCDC8 in Bladder Cancer: Insights from Bioinformatics and Immunohistochemical Analysis
- PMID: 39744495
- PMCID: PMC11685694
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.102655
Prognostic Significance of CCDC8 in Bladder Cancer: Insights from Bioinformatics and Immunohistochemical Analysis
Abstract
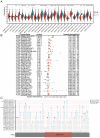
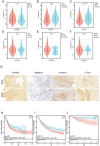
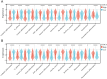
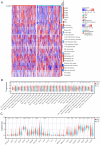
Background: Pro-apoptotic coiled-coil domain containing 8 (CCDC8) has been linked to tumor progression and metastasis, yet its prognostic significance and underlying molecular mechanisms in bladder cancer remain to be elucidated. Materials and methods: This study utilized raw data from public databases along with a single-center retrospective case series. We performed bioinformatics analysis and immunohistochemistry to investigate the biological landscape of CCDC8 in various tumors, with a particular focus on bladder cancer. This involved examining its expression characteristics and prognostic value. Gene function enrichment analysis was conducted to perform functional annotation, evaluate the association between bladder cancer molecular subtypes and mutation spectra, and analyze the tumor immune microenvironment to predict treatment response sensitivity. Results: Our study identified CCDC8 as a novel prognostic marker for bladder cancer. We observed that high CCDC8 expression correlates with poor prognosis and a suboptimal response to immunotherapy in bladder cancer. CCDC8 was implicated in regulating tumor immune status, metabolic activity, and cell cycle-related signaling pathways, thereby influencing the biological behavior of tumor cells. Additionally, CCDC8 contributed to the suppression of the immune microenvironment, diminishing anti-tumor immune responses. Comprehensive characterization of CCDC8 was applied to prognostic prediction in bladder cancer, indicating that targeting CCDC8 may be a potential therapeutic strategy. Conclusions: These findings suggest that CCDC8 serves as an independent biomarker for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy efficacy for bladder cancer. Further investigation into its specific molecular mechanisms may offer new therapeutic strategies for treating bladder cancer.
Keywords: bladder cancer; computational biology and bioinformatics; pro-apoptotic coiled-coil domain containing 8 (CCDC8); tumor microenvironment.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures





Similar articles
-
CDK6 as a Biomarker for Immunotherapy, Drug Sensitivity, and Prognosis in Bladder Cancer: Bioinformatics and Immunohistochemical Analysis.Int J Med Sci. 2024 Sep 16;21(12):2414-2429. doi: 10.7150/ijms.101043. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39310261 Free PMC article.
-
Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 8 inhibits the invasiveness and migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells.Hum Pathol. 2016 Oct;56:64-73. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2016.06.001. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Hum Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27342910
-
JMJD2A sensitizes gastric cancer to chemotherapy by cooperating with CCDC8.Gastric Cancer. 2020 May;23(3):426-436. doi: 10.1007/s10120-019-01024-9. Epub 2019 Nov 1. Gastric Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31677131
-
Prognostic value of COL10A1 and its correlation with tumor-infiltrating immune cells in urothelial bladder cancer: A comprehensive study based on bioinformatics and clinical analysis validation.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 17;14:955949. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.955949. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37006317 Free PMC article.
-
A novel necroptosis-related gene index for predicting prognosis and a cold tumor immune microenvironment in stomach adenocarcinoma.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 27;13:968165. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.968165. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36389725 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Compérat E, Amin MB, Cathomas R, Choudhury A, De Santis M, Kamat A. et al. Current best practice for bladder cancer: a narrative review of diagnostics and treatments. Lancet. 2022;400:1712–21. - PubMed
-
- Grimm M-O, Grün CB, Niegisch G, Pichler M, Roghmann F, Schmitz-Dräger B. et al. Tailored immunotherapy approach with nivolumab with or without ipilimumab in patients with advanced transitional cell carcinoma after platinum-based chemotherapy (TITAN-TCC): a multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023;24:347–59. - PubMed
-
- Malumbres M, Barbacid M. Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:153–66. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

