Dysregulated genes in HIGK-treated F. nucleatum and their possible association with HNSCC
- PMID: 39744516
- PMCID: PMC11624608
- DOI: 10.22099/mbrc.2024.50171.1982
Dysregulated genes in HIGK-treated F. nucleatum and their possible association with HNSCC
Abstract
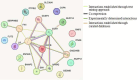
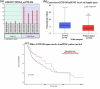
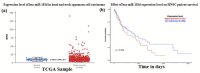
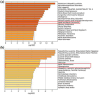
The present study aims to identify the differentially expressed genes in HIGK treated with Fusobacterium nucleatum (Fn) and their possible role in establishing head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. The study design follows a computational approach wherein multiple databases and tools are used to derive the possible association between Fn exposure and the development of HNSCC. The GEOmnibus dataset GSE6927 provided data on the differentially expressed genes in the HIGK treated with Fn. The GEO2R analysis revealed 22 differentially expressed genes in HIGK cells treated with Fn. The expression profile of these genes was then analyzed in the HNSCC (TCGA, Firehose Legacy) dataset employing the UALCAN database. The present study revealed 5 genes viz., GSDMD, NUP214, ZNF426, FUT2, and SERPINB2 exhibiting similar expression patterns in Fn-treated HIGK and HNSCC datasets. The GSDMD and NUP214 were found to be upregulated, and the genes ZNF426, FUT2, and SERPINB2 were downregulated. Among the five genes, the ZNF426 demonstrated a significant association with the survival of HNSCC patients. The low expression of ZNF426 presented a poor prognosis compared to the high expression. The study's results identified ZNF426 as a candidate gene involved in Fusobacterium nucleatum infection and HNSCC. Validating this result is necessary to gain insights into the role of the ZNF426 gene in developing HNSCC. Furthermore, probing the epigenetic factors targeting ZNF426 can be a potential therapeutic lead.
Keywords: Microbes; Cancer; Genotoxicity; Gene expression; Prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Lunger C, Shen Z, Holcombe H, Mannion AJ, Dzink-Fox J, Kurnick S, Feng Y, Muthupalani S, Carrasco SE, Wilson KT, Peek RM, Piazuelo MB, Morgan DR, Armijo AL, Mammoliti M, Wang TC, Fox JG. Gastric coinfection with thiopeptide-positive Cutibacterium acnes decreases FOXM1 and pro-inflammatory biomarker expression in a murine model of Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric cancer. Microbiol Spectr. 2024;12 - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
