Anti-PD1 therapies induce an early expansion of Ki67+CD8+ T cells in metastatic non-oncogene addicted NSCLC patients
- PMID: 39744631
- PMCID: PMC11688303
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1483182
Anti-PD1 therapies induce an early expansion of Ki67+CD8+ T cells in metastatic non-oncogene addicted NSCLC patients
Abstract
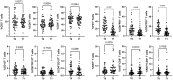
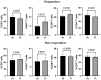
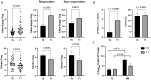
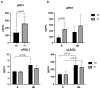
Pembrolizumab (an anti-PD1 antibody) alone or combined with chemotherapy represented the standard of care for advanced non-oncogene addicted non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. These therapies induced early modifications of the immune response impacting the clinical outcome. Identifying early changes in the immune system was critical to directing the therapeutic choice and improving the clinical outcome. In this study, we aim to analyze the activating and inhibiting immune cells of NSCLC patients before and during therapy to identify patients who will benefit from immunotherapies. Forty-eight NSCLC patients were analyzed before (T0) and after the first cycle of immunotherapy (T1), evaluating several activating (CD137+and PD1+), proliferating (Ki67+) and immunosuppressing immune subsets (Tregs: total, active, resting, and non-suppressive; MDSCs: PMN(Lox1+)-MDSC and M-MDSCs) by cytofluorimetry. Concurrently, 14 soluble immune checkpoints were analyzed by Luminex assay. Immunotherapy significantly increased the levels of Ki67+(total and CD8+) T cells, PMN(Lox1+)-MDSCs, non-suppressive Tregs (nsTregs), and soluble PD1 from T0 to T1 in the entire NSCLC population, while decreased active Tregs. These changes were partially attributed to responding patients who showed an increase of Ki67+ and CD8+T cells and nsTregs at T1. CD137+(total, CD8+, and CD4+) T cells and soluble LAG3 were predictor factors at T0 and T1. A low ratio of Tregs/CD137+ T cells and high levels of Ki67+CD137+ T cells positively correlated with response to therapy at T0 and T1, respectively. Results highlighted that immunotherapy improved the immunological fitness of those patients who benefited from immunotherapy, changing the immunological balance towards immune activation.
Keywords: CD137; NSCLC; anti-PD-1; immune checkpoint inhibitors; lymphocytes.
Copyright © 2024 Gelibter, Tuosto, Asquino, Siringo, Sabatini, Zizzari, Pace, Scirocchi, Valentino, Bianchini, Caponnetto, Paoli, Bellati, Santini, Nuti, Rughetti and Napoletano.
Conflict of interest statement
MS reports travel grants from Novartis grants and speaker’s honoraria. AG received speaker’s honoraria from and participated on the advisory board from AstraZeneca, MSD, Roche, BMS, Takeda. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sezer A, Kilickap S, Gümüş M, Bondarenko I, Özgüroğlu M, Gogishvili M, et al. Cemiplimab monotherapy for first-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with PD-L1 of at least 50%: a multicentre, open-label, global, phase 3, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet. (2021) 397:592–604. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(21)00228-2 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

