Orchestrating the frontline: HDAC3-miKO recruits macrophage reinforcements for accelerated myelin debris clearance after stroke
- PMID: 39744685
- PMCID: PMC11671378
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.103449
Orchestrating the frontline: HDAC3-miKO recruits macrophage reinforcements for accelerated myelin debris clearance after stroke
Abstract
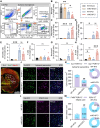
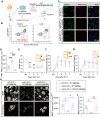
Rational: White matter has emerged as a key therapeutic target in ischemic stroke due to its role in sensorimotor and cognitive outcomes. Our recent findings have preliminarily revealed a potential link between microglial HDAC3 and white matter injury following stroke. However, the mechanisms by which microglial HDAC3 mediates these effects remain unclear. Methods : We generated microglia-specific HDAC3 knockout mice (HDAC3-miKO). DTI, electrophysiological technique and transmission electron microscopy were used to assess HDAC3-miKO's effects on white matter. RNA sequencing, flow cytometry, immunofluorescence staining and ex vivo phagocytosis assay were conducted to investigate the mechanism by which HDAC3-miKO ameliorated white matter injury. Macrophage depletion and reconstitution experiments further confirmed the involvement of macrophage CCR2 in the enhanced white matter repair and sensorimotor function in HDAC3-miKO mice. Results : HDAC3-miKO promoted post-stroke oligodendrogenesis and long-term histological and functional integrity of white matter without affecting early-stage white matter integrity. In the acute phase, HDAC3-deficient microglia showed enhanced chemotaxis, recruiting macrophages to the infarct core probably by CCL2/CCL7, where dMBP-labelled myelin debris surged and coincided with their infiltration. Infiltrated macrophages outperformed resident microglia in myelin phagocytosis, potentially serving as true pioneers in myelin debris clearance. Although macrophage phagocytosis potential was similar between HDAC3-miKO and WT mice, increased macrophage numbers in HDAC3-miKO accelerated myelin debris clearance. Reconstitution with CCR2-KO macrophages in HDAC3-miKO mice slowed this clearance, reversing HDAC3-miKO's beneficial effects. Conclusions : Our study demonstrates that HDAC3-deficient microglia promote post-stroke remyelination by recruiting macrophages to accelerate myelin debris clearance, underscoring the essential role of infiltrated macrophages in HDAC3-miKO-induced beneficial outcomes. These findings advance our understanding of microglial HDAC3's role and suggest therapeutic potential for targeting microglial HDAC3 in ischemic stroke.
Keywords: HDAC3-miKO; chemotaxis; macrophages; myelin debris; white matter repair.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures





References
-
- Yuan C, Shi L, Sun Z, Xu F, Wang C, Shan J. et al. Regulatory T cell expansion promotes white matter repair after stroke. Neurobiol Dis. 2023;179:106063. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

