Effects of Isalo scorpion cytotoxic peptide on growth, immune performance, and intestinal flora of yellow-feathered broilers
- PMID: 39744713
- PMCID: PMC11688812
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1511680
Effects of Isalo scorpion cytotoxic peptide on growth, immune performance, and intestinal flora of yellow-feathered broilers
Abstract
Introduction: This study aimed to investigate the effects of Isalo scorpion cytotoxic peptide (IsCT) on the growth performance, immune function, and gut microbiota of yellow-feathered broilers.
Methods: The experiment involved supplementing a corn-soybean meal-based diet with various dietary levels of IsCT. The experiment adopted a completely randomized design. A total of 240 one-day-old yellow-feathered broilers were randomly divided into six groups: a control group (CON), a chlortetracycline group (CTC), and four groups receiving a basal diet with 50, 100, 150, or 200 mg/ kg IsCT (IsCT50, IsCT100, IsCT150, and IsCT200). The trial period lasted 60 days.
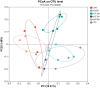
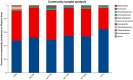
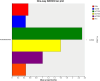
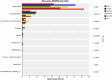
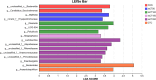
Results: The results showed that the average final body weight and average daily weight gain of the IsCT150 and IsCT200 groups were significantly higher than those of the CON group (p < 0.05). Compared to the CTC group, the average daily feed intake in group III was significantly lower (p < 0.05). The feed conversion ratios of the IsCT150 and IsCT200 groups were significantly lower than those of the IsCT50 and CON groups (p < 0.05). Albumin levels in the CTC and IsCT150 groups were significantly higher than those in the CON, IsCT100, and IsCT50 groups. Alanine transaminase levels in the IsCT150 group were significantly lower than those in the IsCT50, IsCT200, CON, and CTC groups (p < 0.05), but there was no significant difference compared with the IsCT100 group (p < 0.05). IgA levels in the IsCT150, IsCT200, and CTC groups were significantly higher than those in the IsCT50 group (p < 0.05). IgG levels in the CTC, IsCT100, IsCT150, and IsCT200 groups were significantly higher than those in the IsCT50 and CON groups (p < 0.05). 16S rRNA sequencing indicated significant differences in the caecal microbiota between the IsCT and CON groups (p < 0.05). The abundance of Bacteroidetes increased, whereas that of Firmicutes decreased in the IsCT groups; however, the difference was not significant (p < 0.05). The relative abundances of Actinobacteriota and Patescibacteria were significantly different in the IsCT100 group (p < 0.05).
Discussion: In conclusion, supplementing the basal diet with IsCT improved growth performance, immune function, and gut microbiota of yellow-feathered broilers at an optimal supplementation level of 150 mg/kg.
Keywords: ISCT; antimicrobial peptide; broilers; growth; gut microbiota; immune.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Ma, Liu, Zhu, Chen, Gao, Wang, Wang and Shen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of dietary Brassica rapa L. polysaccharide on growth performance, immune and antioxidant functions and intestinal flora of yellow-feathered quail.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 16;14(1):28252. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77017-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39548157 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of dietary ellagic acid supplementation on growth performance, immune response, antioxidant activity, digestive enzyme activities, and intestinal functions in yellow-feathered broilers.J Anim Sci. 2022 Dec 1;100(12):skac301. doi: 10.1093/jas/skac301. J Anim Sci. 2022. PMID: 36074562 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of maggot antimicrobial peptides on growth performance, immune function, and cecal flora of yellow-feathered broilers.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Jul 25;10:1156964. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1156964. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37559887 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dietary polyherbal mixtures on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, immune function and jejunal health of yellow-feathered broilers.Poult Sci. 2023 Jul;102(7):102714. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102714. Epub 2023 Apr 12. Poult Sci. 2023. PMID: 37172360 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Taraxacum mongolicum Hand.-Mazz. (dandelion) on growth performance, expression of genes coding for tight junction protein and mucin, microbiota composition and short chain fatty acids in ileum of broiler chickens.BMC Vet Res. 2022 May 14;18(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s12917-022-03278-5. BMC Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 35568942 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu D, Cui D, Zhou M, Ying Y. Information perception in modern poultry farming: a review. Comput Electron Agric. (2022) 199:107131. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2022.107131 - DOI
-
- FAO . Food and agriculture organization of the United Nations, Rome, pp. 403–403. (2018). Available at: http://faostat.fao.org.
-
- English BK, Gaur AH. The use and abuse of antibiotics and the development of antibiotic resistance In: Finn A, Curtis N, Pollard AJ, editors. Hot topics in infection and immunity in children VI. New York: Springer; (2010). 73–82.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

