In Vivo Evidence for the Preventive Role of Vaccinium macrocarpon Aiton in Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Ulcer: Focusing on Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Apoptotic Mechanisms
- PMID: 39745481
- PMCID: PMC11694502
- DOI: 10.1002/vms3.70048
In Vivo Evidence for the Preventive Role of Vaccinium macrocarpon Aiton in Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Ulcer: Focusing on Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Apoptotic Mechanisms
Abstract
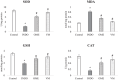
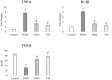
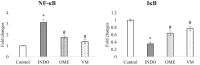
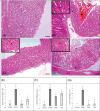
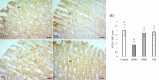
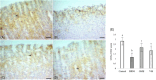
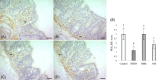
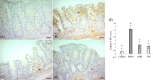
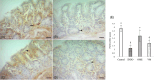
The present study aimed to unveil the gastroprotective potential of Vaccinium macrocarpon (VM) extract and its mechanism of action against indomethacin (INDO)-induced gastric ulcers in rats. To achieve this goal, rats were pretreated with either omeprazole (20 mg/kg) or VM (100 mg/kg) orally for 14 consecutive days. Gastric tissue samples were collected and various parameters were evaluated to understand the mechanism of VM's action, including the levels of superoxide dismutase, malondialdehyde, glutathione, CAT and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), as well as the mRNA expression levels of tumour necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1 beta, nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) and inhibitor kappa B (IκB). Additionally, the immunopositivity of cyclooxygenase (COX)-1, COX-2, PGE2, proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) and caspase-3 was assessed. The total amount of phenolic compounds present in the VM extract was high (58.08 µg/mL gallic acid equivalent/mg extract). The healing effect of VM was demonstrated by an increase in the expression of PCNA. Furthermore, the level of TGF-β was found to increase upon treatment with VM. Analyses of COX-1, COX-2 and PGE2 expression in gastric tissue confirmed the gastroprotective effect of VM. Notably, the expression of NF-κB was markedly reduced, whereas that of IκB was substantially increased. Overall, the findings of this study demonstrate that VM extract has gastroprotective and curative effects against INDO-induced ulcers through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, mucosal regenerative and anti-apoptotic activities. Therefore, VM may serve as a useful adjuvant treatment for nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs-induced gastric ulcer disease.
Keywords: cyclooxygenase (COX); nuclear factor kappa B (NF‐κB)/inhibitor kappa B (IκB); oxidative stress; ulcer; vaccinium macrocarpon.
© 2025 The Author(s). Veterinary Medicine and Science published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Albensi, B. C. , and Mattson M. P.. 2000. “Evidence for the Involvement of TNF and NF‐KappaB in Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity.” Synapse 35, no. 2: 151–159. - PubMed
-
- Ali Khan, M. S. , Nazan S., and Mat Jais A. M.. 2017. “Flavonoids and Anti‐Oxidant Activity Mediated Gastroprotective Action of Leathery Murdah, Terminalia coriacea (Roxb.) Wight & Arn. Leaf Methanolic Extract in Rats.” Arquivos de Gastroenterologia 54, no. 3: 183–191. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

