The SwiftScan step-and-shoot continuous mode improves SPECT scanning efficiency: a preliminary phantom and clinical test
- PMID: 39745654
- PMCID: PMC11695528
- DOI: 10.1186/s40658-024-00709-0
The SwiftScan step-and-shoot continuous mode improves SPECT scanning efficiency: a preliminary phantom and clinical test
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of the study was to investigate the value of SwiftScan Step-and-Shoot Continuous (SSC) scanning mode in enhancing image quality and to explore appropriate scanning parameters for reducing scan time.
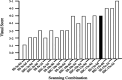
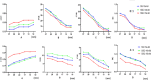
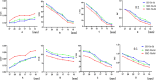
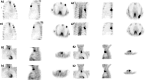
Methods: This study was composed of a phantom study and two clinical tests. The differences in visual image quality scores, coefficient of variance (COV) of the background, image signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR), and recovery coefficient (RC) of the sphere were compared between SSC mode and traditional Step-and-Shoot (SS) mode in the phantom study. Various "shoot" acquisition times (5s, 10s, 15s) and "step" angles (3-degree, 6-degree, 9-degree) were evaluated and verified. In the clinical tests, bone tomography and parathyroid tomography were performed on 30 patients each. Differences in visual image quality scores, background COV, image SNR, CNR, and standardized uptake value (SUV) of lesions were compared between the two modes.
Results: In the phantom study, SSC mode demonstrated higher visual scores and significantly reduced background COV (P < 0.05), and significantly increased SNR and CNR (P < 0.05) compared to SS mode. No significant alteration in RC was observed (P > 0.05). In the clinical tests, no significant differences were found between the optimal SSC scan combination (10s "shoot" and 6-degree "step")/ (10s "shoot" and 3-degree "step") and the traditional SS scan combination (15s "shoot" and 6-degree "step")/ (15s "shoot" and 3-degree "step") in visual image quality scores, background COV, image SNR, CNR, and SUV of bone and parathyroid high uptake lesions (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: The SwiftScan SSC mode can reduce acquisition time by 33% while maintaining similar image quality and quantification accuracy compared to SS mode. An SSC scanning protocol with a 10s "shoot" acquisition and 6-degree "step" or with a 10s "shoot" acquisition and 3-degree "step" over a 360-degree rotation, is recommended for clinical use.
Keywords: Acquisition efficiency; Image quality; SPECT/CT; Step-and-shoot continuous mode; SwiftScan.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This article does not contain any experiments with animals. All procedures involving human participants were carried out in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Second Hospital of Lanzhou University [2024A-799]. Consent for publication: Written informed consent was obtained from all patients in the study. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Conflict of interest there are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Agency IAE. Clinical Applications of SPECT: New Hybrid Nuclear Medicine Imaging System. International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA); 2008.
-
- Cao Z, Maunoury C, Chen CC, Holder LE. Comparison of continuous step-and-shoot versus step-and-shoot acquisition SPECT. J Nucl Med Off Publ Soc Nucl Med. 1996;37:2037–40. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

