Blue Light Damages Retinal Ganglion Cells Via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Autophagy in Chickens
- PMID: 39745679
- PMCID: PMC11702841
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.66.1.3
Blue Light Damages Retinal Ganglion Cells Via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Autophagy in Chickens
Abstract
Purpose: Because chickens have excellent light perception properties, this study focused on investigating whether monochromatic light can cause photodamage in chicken retinal ganglion cells (RGCs).
Methods: Post-hatching day chickens were exposed to four different light-emitting diode light environments for five weeks, respectively, monochromatic blue light (480 nm), green light (560 nm), red light (660 nm), or white light (6000 K). The mechanisms through which monochromatic light influences the structure of the chicken retina were analyzed by detecting the morphological structure of the retina, gene and protein expression levels, and the ultrastructure of the optic nerve.
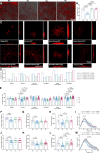
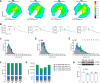
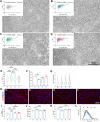
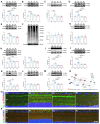
Results: Blue light exposure for five weeks significantly impacted the thickness of the inner reticular layer, retinal synaptic function, and the number of RGCs in the chicken retina. Moreover, neurodegenerative disease characteristics, such as a reduction in the number of dendritic branches and the presence of myelin lesions, have also been observed in RGCs. The activation of the protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase-mediated unfolded protein response, along with the abnormal degradation of the autophagy substrate P62, accompanies these retinal pathological processes. Additionally, our findings indicate that the photosensitivity of OPN4 is linked to endoplasmic reticulum stress in RGCs, which may elucidate why chicken RGCs experience damage exclusively under blue light exposure.
Conclusions: Blue light can damage the chicken retina through endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy, especially in RGCs. Our study enhances the understanding of the mechanisms underlying retinal photodamage and emphasizes the risk of retinal damage in low-illuminance blue light environments.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures


References
-
- Wang L, Yu X, Zhang D, et al.. Long-term blue light exposure impairs mitochondrial dynamics in the retina in light-induced retinal degeneration in vivo and in vitro. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2023; 240: 112654. - PubMed
-
- Godley BF, Shamsi FA, Liang FQ, et al.. Blue light induces mitochondrial DNA damage and free radical production in epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280: 21061–21066. - PubMed
-
- Wenzel A, Grimm C, Samardzija M, Reme CE. Molecular mechanisms of light-induced photoreceptor apoptosis and neuroprotection for retinal degeneration. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2005; 24: 275–306. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

