Polymerase-usage sequencing identifies initiation zones with less bias across S phase in mouse embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 39745849
- PMCID: PMC11879308
- DOI: 10.1093/jb/mvae097
Polymerase-usage sequencing identifies initiation zones with less bias across S phase in mouse embryonic stem cells
Abstract
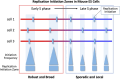
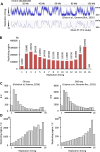
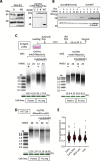
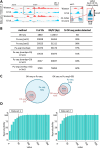
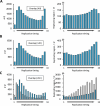
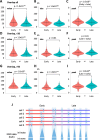
Various methods have been developed to map replication initiation zones (IZs) genome-wide, often finding far fewer IZs than expected. In particular, IZs corresponding to later stages of S phase are under-represented. Here, we reanalysed IZs with respect to replication timing in mouse ES cells. These datasets identified over five times as many early IZs compared to late IZs. In addition, we have set up a polymerase-usage sequencing (Pu-seq) system in mouse ES cells to map IZs genome-wide. Pu-seq showed less bias towards early IZs, potentially indicating better sensitivity for identifying IZs in late S phase.
Keywords: DNA replication; mouse embryonic stem cells; polymerase-usage sequencing; replication initiation zones; replication timing.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Japanese Biochemical Society.
Figures
References
-
- Chagin, V.O., Casas-Delucchi, C.S., Reinhart, M., Schermelleh, L., Markaki, Y., Maiser, A., Bolius, J.J., Bensimon, A., Fillies, M., Domaing, P., Rozanov, Y.M., Leonhardt, H., and Cardoso, M.C. (2016) 4D visualization of replication foci in mammalian cells corresponding to individual replicons. Nat. Commun. 7, 11231. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nakamura, H., Morita, T., and Sato, C. (1986) Structural organizations of replicon domains during DNA synthetic phase in the mammalian nucleus. Exp. Cell Res. 165, 291–297 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

