Metronomic Capecitabine Plus Aromatase Inhibitor as Initial Therapy in Patients With Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer: The Phase III MECCA Trial
- PMID: 39746176
- PMCID: PMC11974638
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.24.00938
Metronomic Capecitabine Plus Aromatase Inhibitor as Initial Therapy in Patients With Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer: The Phase III MECCA Trial
Abstract
Purpose: The effects of metronomic chemotherapy plus endocrine therapy have yet to be elucidated through a randomized phase III clinical trial.
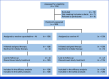
Methods: Randomized clinical trials were conducted at 12 centers in China from August 22, 2017, to September 24, 2021, and the final follow-up date was August 25, 2023. Patients with hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative metastatic breast cancer (MBC) who had no previous systemic therapy in the metastatic setting were enrolled. Participants were 1:1 assigned to receive either metronomic capecitabine plus an aromatase inhibitor (AI) or AI alone. The primary end point was progression-free survival (PFS). Secondary end points included overall survival (OS), objective response rate, disease control rate (defined as disease controlled for ≥24 weeks), and safety.
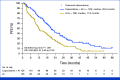
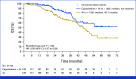
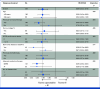
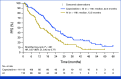
Results: A total of 263 patients were randomly assigned, among which 254 patients formed the full analysis set. At the median follow-up time of 50.7 months, 203 PFS events occurred. The metronomic capecitabine plus AI arm exhibited a median PFS of 20.9 months compared with 11.9 months in the AI arm (hazard ratio [HR], 0.58 [95% CI, 0.43 to 0.76]). The median OS was not reached in the combination arm and was 45.1 months in the AI arm (HR, 0.58 [95% CI, 0.37 to 0.93]). The most common adverse events were palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia and peripheral neuropathy; grade 3 events occurred in 15.1% of the patients receiving combination treatment.
Conclusion: The MECCA trial demonstrated a significant improvement in PFS and OS with first-line metronomic capecitabine plus AI compared with AI alone in patients with hormone receptor-positive+/HER2-negative MBC. Both treatment arms exhibited tolerable safety profiles consistent with previous reports.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02767661.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures
References
-
- Rugo HS, Rumble RB, Macrae E, et al. : Endocrine therapy for hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology guideline. J Clin Oncol 34:3069-3103, 2016 - PubMed
-
- Sledge GW Jr, Toi M, Neven P, et al. : MONARCH 2: Abemaciclib in combination with fulvestrant in women with HR+/HER2- advanced breast cancer who had progressed while receiving endocrine therapy. J Clin Oncol 35:2875-2884, 2017 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

