Innovation of a Neonatal Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter to Expand Dialysis Capabilities for Critically Ill Neonates in Low-Resource Settings
- PMID: 39746338
- PMCID: PMC11949190
- DOI: 10.1159/000542613
Innovation of a Neonatal Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter to Expand Dialysis Capabilities for Critically Ill Neonates in Low-Resource Settings
Abstract
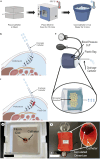
Introduction: The lack of peritoneal dialysis (PD) catheters designed explicitly for neonates creates significant challenges in the provision of neonatal PD. High resource settings can circumvent this limitation by resorting to alternative extracorporeal dialysis methods. However, in low-resource settings, PD remains the preferred dialysis modality, and the use of off-label catheters for PD results in complications such as omental wrapping and occlusion. This study introduces a novel catheter design featuring a multi-diameter side port configuration and a helical geometry.
Methods: We employed numerical simulations to identify an optimal multi-diameter side port configuration, to address fluid dynamic issues that lead to catheter occlusion and omental wrapping. Following the simulations, we experimentally evaluated the catheter's performance in a series of benchtop tests designed to simulate physiological conditions encountered in neonatal PD.
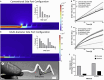
Results: Our experimental evaluations demonstrated that the helical catheter outperforms commonly utilized pigtail catheters with same-sized diameter side ports by consistently achieving superior drainage efficiency during fibrin clot occlusion and omental wrapping tests.
Conclusion: The catheter is intended to be placed at the bedside to perform renal replacement therapy for neonates in low-resourced settings.
Introduction: The lack of peritoneal dialysis (PD) catheters designed explicitly for neonates creates significant challenges in the provision of neonatal PD. High resource settings can circumvent this limitation by resorting to alternative extracorporeal dialysis methods. However, in low-resource settings, PD remains the preferred dialysis modality, and the use of off-label catheters for PD results in complications such as omental wrapping and occlusion. This study introduces a novel catheter design featuring a multi-diameter side port configuration and a helical geometry.
Methods: We employed numerical simulations to identify an optimal multi-diameter side port configuration, to address fluid dynamic issues that lead to catheter occlusion and omental wrapping. Following the simulations, we experimentally evaluated the catheter's performance in a series of benchtop tests designed to simulate physiological conditions encountered in neonatal PD.
Results: Our experimental evaluations demonstrated that the helical catheter outperforms commonly utilized pigtail catheters with same-sized diameter side ports by consistently achieving superior drainage efficiency during fibrin clot occlusion and omental wrapping tests.
Conclusion: The catheter is intended to be placed at the bedside to perform renal replacement therapy for neonates in low-resourced settings.
Keywords: Low- and middle-income countries; Neonatal acute kidney injury; Peritoneal dialysis.
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
Cook Medical provided material support by supplying stock catheter tubing for test samples. Carl Russell III was employed by Cook Medical between August 2020 and August 2022.
Figures
References
-
- Nourse P, Cullis B, Finkelstein F, Numanoglu A, Warady B, Antwi S, et al. ISPD guidelines for peritoneal dialysis in acute kidney injury: 2020 Update (paediatrics). Perit Dial Int. 2021;41(2):139–57. - PubMed
-
- McCulloch M, Luyckx VA, Cullis B, Davies SJ, Finkelstein FO, Yap HK, et al. Challenges of access to kidney care for children in low-resource settings. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021;17(1):33–45. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

