Invasion of glioma cells through confined space requires membrane tension regulation and mechano-electrical coupling via Plexin-B2
- PMID: 39747004
- PMCID: PMC11697315
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55056-6
Invasion of glioma cells through confined space requires membrane tension regulation and mechano-electrical coupling via Plexin-B2
Abstract
Glioblastoma (GBM) is a malignant brain tumor with diffuse infiltration. Here, we demonstrate how GBM cells usurp guidance receptor Plexin-B2 for confined migration through restricted space. Using live-cell imaging to track GBM cells negotiating microchannels, we reveal endocytic vesicle accumulation at cell front and filamentous actin assembly at cell rear in a polarized manner. These processes are interconnected and require Plexin-B2 signaling. We further show that Plexin-B2 governs membrane tension and other membrane features such as endocytosis, phospholipid composition, and inner leaflet surface charge, thus providing biophysical mechanisms by which Plexin-B2 promotes GBM invasion. Together, our studies unveil how GBM cells regulate membrane tension and mechano-electrical coupling to adapt to physical constraints and achieve polarized confined migration.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: K.D. Costa discloses his role as scientific co-founder and Chief Scientific Officer of Novoheart, Medera Inc. NovoHeart did not play any role in the design, conduct, or funding of this study. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



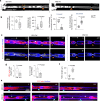
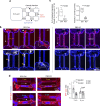
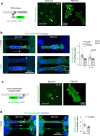
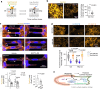
Update of
-
Invasion of glioma cells through confined space requires membrane tension regulation and mechano-electrical coupling via Plexin-B2.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 2:2024.01.02.573660. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.02.573660. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 2;16(1):272. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55056-6. PMID: 38313256 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS107462/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS092735/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- R01 NS134159/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 NS127948/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS134158/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- C39068GG/New York State Department of Health (NYS Department of Health)
- R01 NS092735/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS125700/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- NS107462/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- C38330GG/New York State Department of Health (NYS Department of Health)
- S10 RR027609/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- NS134159/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- R21 NS125700/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD021838/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- NS127948/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

