Mitochondrial-cytochrome c oxidase II promotes glutaminolysis to sustain tumor cell survival upon glucose deprivation
- PMID: 39747079
- PMCID: PMC11695821
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55768-9
Mitochondrial-cytochrome c oxidase II promotes glutaminolysis to sustain tumor cell survival upon glucose deprivation
Abstract
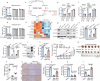
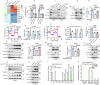
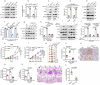
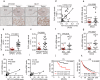
Glucose deprivation, a hallmark of the tumor microenvironment, compels tumor cells to seek alternative energy sources for survival and growth. Here, we show that glucose deprivation upregulates the expression of mitochondrial-cytochrome c oxidase II (MT-CO2), a subunit essential for the respiratory chain complex IV, in facilitating glutaminolysis and sustaining tumor cell survival. Mechanistically, glucose deprivation activates Ras signaling to enhance MT-CO2 transcription and inhibits IGF2BP3, an RNA-binding protein, to stabilize MT-CO2 mRNA. Elevated MT-CO2 increases flavin adenosine dinucleotide (FAD) levels in activating lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) to epigenetically upregulate JUN transcription, consequently promoting glutaminase-1 (GLS1) and glutaminolysis for tumor cell survival. Furthermore, MT-CO2 is indispensable for oncogenic Ras-induced glutaminolysis and tumor growth, and elevated expression of MT-CO2 is associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer patients. Together, these findings reveal a role for MT-CO2 in adapting to metabolic stress and highlight MT-CO2 as a putative therapeutic target for Ras-driven cancers.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

