Integrating genetic subtypes with PET scan monitoring to predict outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 39747123
- PMCID: PMC11696268
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55614-y
Integrating genetic subtypes with PET scan monitoring to predict outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
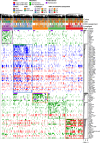
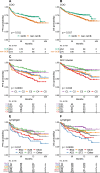
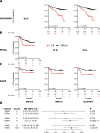
Next Generation Sequencing-based subtyping and interim- and end of treatment positron emission tomography (i/eot-PET) monitoring have high potential for upfront and on-treatment risk assessment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients. We performed Dana Farber Cancer Institute (DFCI) and LymphGen genetic subtyping for the HOVON84 (n = 208, EudraCT-2006-005174-42) and PETAL (n = 204, EudraCT-2006-001641-33) trials retrospectively combined with DFCI genetic data (n = 304). For all R-CHOP treated patients (n = 592), C5/MCD- and C2/A53-subtypes show significantly worse outcome independent of the international prognostic index. For all subtypes, adverse prognostic value of i/eot-PET-positive status is confirmed. Consistent with frequent primary refractory disease, only 67% C2 patients become eot-PET-negative versus 81-88% for other subtypes. Indicative of high relapse rates, outcome of C5 i/eot-PET-negative patients remains significantly worse in HOVON-84, which trend validates in the PETAL and SAKK38-07 trials (NCT00544219). These results show the added value of integrated genetic subtyping and PET monitoring for prognostic stratification and subtype-specific trial design.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Shipp, M. A. & Harrington, D. P. A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med.329, 987–994 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Van Imhoff, G. W. et al. Ofatumumab versus rituximab salvage chemoimmunotherapy in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: The ORCHARRD study. J. Clin. Oncol.35, 544–551 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

