Structural basis for catalysis and selectivity of phospholipid synthesis by eukaryotic choline-phosphotransferase
- PMID: 39747155
- PMCID: PMC11696302
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55673-1
Structural basis for catalysis and selectivity of phospholipid synthesis by eukaryotic choline-phosphotransferase
Abstract
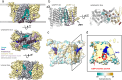
Phospholipids are the most abundant component in lipid membranes and are essential for the structural and functional integrity of the cell. In eukaryotic cells, phospholipids are primarily synthesized de novo through the Kennedy pathway that involves multiple enzymatic processes. The terminal reaction is mediated by a group of cytidine-5'-diphosphate (CDP)-choline /CDP-ethanolamine-phosphotransferases (CPT/EPT) that use 1,2-diacylglycerol (DAG) and CDP-choline or CDP-ethanolamine to produce phosphatidylcholine (PC) or phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) that are the main phospholipids in eukaryotic cells. Here we present the structure of the yeast CPT1 in multiple substrate-bound states. Structural and functional analysis of these binding-sites reveal the critical residues for the DAG acyl-chain preference and the choline/ethanolamine selectivity. Additionally, we present the structure in complex with a potent inhibitor characterized in this study. The ensemble of structures allows us to propose the reaction mechanism for phospholipid biosynthesis by the family of CDP-alcohol phosphotransferases (CDP-APs).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: S.M. is an employee of Xaira Therapeutics. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

