Discovering natural products as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins
- PMID: 39747174
- PMCID: PMC11697186
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-83637-4
Discovering natural products as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins
Abstract
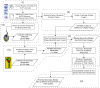
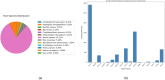
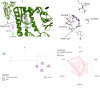
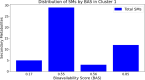
The ongoing global pandemic caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus has demanded the urgent search for effective therapeutic interventions. In response, our research aimed at identifying natural products (NPs) with potential inhibitory effects on the entry of the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein into host cells. Utilizing the Protein Data Bank Japan (PDBJ) and BindingDB databases, we isolated 204 S-glycoprotein sequences and conducted a clustering analysis to identify similarities and differences among them. We subsequently identified 33,722 binding molecules (BMs) by matching them with the sequences of 204 S-glycoproteins and compared them with 52,107 secondary metabolites (SMs) from the KNApSAcK database to identify potential inhibitors. We conducted docking and drug-likeness property analyses to identify several SMs with potential as drug candidates based on binding energy (BE), no Lipinski's rule violation (LV), psychochemical properties within the pink area of the bioavailability radar, and a bioavailability score (BAS) not less than 0.55. Fourteen SMs were predicted through computational analysis as potential candidates for inhibiting the three major types of S proteins. Our study provides a foundation for further experimental validation of these compounds as potential therapeutic agents against SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: Drug discovery; Natural products; SARS-CoV-2; Spike protein; Virtual screening.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Rastawicki, W. & Rokosz-Chudziak, N. Characteristics and assessment of the usefulness of serological tests in the diagnostic of infections caused by coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 on the basis of available manufacturer’s data and literature review. Przegl Epidemiol.74(1), 49–68. 10.32394/pe.74.11 (2020). - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

