Multiparametric MRI along with machine learning predicts prognosis and treatment response in pediatric low-grade glioma
- PMID: 39747214
- PMCID: PMC11697432
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55659-z
Multiparametric MRI along with machine learning predicts prognosis and treatment response in pediatric low-grade glioma
Abstract
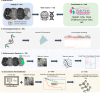
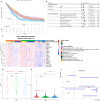
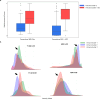
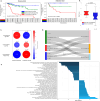
Pediatric low-grade gliomas (pLGGs) exhibit heterogeneous prognoses and variable responses to treatment, leading to tumor progression and adverse outcomes in cases where complete resection is unachievable. Early prediction of treatment responsiveness and suitability for immunotherapy has the potential to improve clinical management and outcomes. Here, we present a radiogenomic analysis of pLGGs, integrating MRI and RNA sequencing data. We identify three immunologically distinct clusters, with one group characterized by increased immune activity and poorer prognosis, indicating potential benefit from immunotherapies. We develop a radiomic signature that predicts these immune profiles with over 80% accuracy. Furthermore, our clinicoradiomic model predicts progression-free survival and correlates with treatment response. We also identify genetic variants and transcriptomic pathways associated with progression risk, highlighting links to tumor growth and immune response. This radiogenomic study in pLGGs provides a framework for the identification of high-risk patients who may benefit from targeted therapies.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 75N91019D00024/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U2C HL156291/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U2C HL156291/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U2C HL156291/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U2C HL156291/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U2C HL156291/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U2C HL156291/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U2C HL156291/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U2C HL156291/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U2C HL156291/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U2C HL156291/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U2C HL156291/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U2C HL156291/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

