Comprehensive analysis of heat shock protein 110, 90, 70, 60 families and tumor immune microenvironment characterization in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 39747468
- PMCID: PMC11697189
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-84834-x
Comprehensive analysis of heat shock protein 110, 90, 70, 60 families and tumor immune microenvironment characterization in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
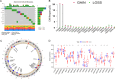
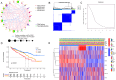
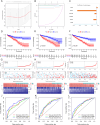
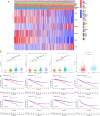
Heat shock proteins (HSPs) are a kind of molecular chaperone that helps protein folding, which is closely related to cancer. However, the association between HSPs and clear cell renal clear cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is uncertain. We explored the prognostic value of HSP110, HSP90, HSP70 and HSP60 families in ccRCC and their role in tumor immune microenvironment. The data obtained from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) were applied to determine the differential expression of HSPs in normal tissues and ccRCC. We comprehensively analyzed the prognostic value of HSPs in ccRCC and constructed a prognostic signature. We further explored the differences of tumor immune microenvironment and targeted therapy based on the signature. Cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis were detected by CCK8 assay, wound healing and transwell. Three clusters were identified with differences in overall survival and tumor stage. 6-gene signature (HSPA8, HSP90B1, HSPA7, HSPA12B, HSPA4L, HSPA1L) was identified to predict ccRCC patients' prognosis. The signature was confirmed in the internal cohort. Survival analysis, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, univariate and multivariate COX regression analysis demonstrated the accuracy and independence of signature. The expression of HSPA7, HSPA8 and HSP90B1 were validated with quantitative real-time PCR. Our signature played a pivotal role in predicting tumor immune microenvironment, immune checkpoint gene expression, drug sensitivity, and tumor mutational burden (TMB) in patients with ccRCC. Our cellular experiments confirmed HSPA7 promotes the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of ccCRC cells. The HSPs signature identified in this study could serve as potential biomarkers for predicting prognosis and treatment response in ccRCC patients. It may provide new ideas for the current research on targeted therapy and immunotherapy strategies for ccRCC patients.
Keywords: Clear cell renal cell carcinoma; Drug sensitivity; Heat shock protein; Immune checkpoints; Prognostic signature; Tumor immune microenvironment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comprehensive insights on pivotal prognostic signature involved in clear cell renal cell carcinoma microenvironment using the ESTIMATE algorithm.Cancer Med. 2020 Jun;9(12):4310-4323. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2983. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 32311223 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of prognostic biomarkers in ccRCC: immune-stromal score and survival prediction.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jan 27;25(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13534-0. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39871215 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Analysis of Immune- and Metabolism-Related Genes Identifies Robust Prognostic Signature and PYCR1 as a Carcinogenic Regulator in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 21;26(10):4953. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104953. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40430095 Free PMC article.
-
HSPA8 and HSPA9: Two prognostic and therapeutic targets in breast, colon, and kidney cancers?Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2025 Aug;1871(6):167827. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2025.167827. Epub 2025 Apr 4. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2025. PMID: 40189113 Review.
-
Biomarker-informed care for patients with renal cell carcinoma.Nat Cancer. 2025 Apr;6(4):573-583. doi: 10.1038/s43018-025-00942-1. Epub 2025 Apr 16. Nat Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40240621 Review.
References
-
- Hsieh, J. J. et al. Genomic classifications of renal cell carcinoma: A critical step towards the future application of personalized kidney cancer care with pan-omics precision. J. Pathol.244 (5), 525–537. 10.1002/path.5022 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Wallis, C. J. D. et al. First-line systemic therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Eur. Urol.74 (3), 309–321. 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.03.036 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Rini, B. I., Campbell, S. C. & Escudier, B. Ren. cell. Carcinoma Lancet, 373(9669): 1119–1132. DOI: 10.1016/s0140-6736(09)60229-4. (2009). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

