Narrative mobile video game-based cognitive training to enhance frontal function in patients with mild cognitive impairment
- PMID: 39747611
- PMCID: PMC11696466
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-84086-9
Narrative mobile video game-based cognitive training to enhance frontal function in patients with mild cognitive impairment
Abstract
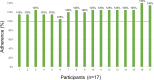
Although cognitive training has been proposed as a possible therapeutic modality for mild cognitive impairment (MCI), most serious games focus on specific tasks. This study aimed to investigate the feasibility and efficacy of narrative video game-based cognitive intervention for MCI. A four-week (± 1-week) mobile game intervention was given to 17 MCI participants (mean age (SD) = 72.8(4.75)). At baseline and post-intervention, the participants received neuropsychological tests and a depression scale. Frontal function was assessed using the Corsi block-tapping test, Color Word Stroop Test, Controlled Oral Word Association Test, Digit Symbol Coding, and Trail Making Test-Elderly's Version; depression was assessed using the Geriatric Depression Scale. User's compliance and gaming experience were also evaluated. MCI patients showed significant improvements in frontal function, particularly in Digit Symbol Coding (mean ± SD, 0.47 ± 0.49, p = 0.007) and phonemic fluency (mean ± SD, 0.39 ± 0.55, p = 0.024). Each frontal subtest's mean z-score was increased (mean ± SD, 0.44 ± 0.38, p = 0.008). Block span and depression scale remained unchanged. High adherence rates (122.35%) and favorable feedback on the gaming experience indicated that the game intervention's usability boosted patients' motivation and engagement. Our findings demonstrate that narrative game-based cognitive intervention was not only beneficial but also enjoyable for elderly MCI.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: Nunaps Inc. supported this study and participated in the conceptualization, design, and development of the digital therapeutic used in this research. The authors declare the following potential competing interests: JSL and JHL have no competing interests. CYS and DK were former employees of Nunaps Inc. during the study period. HC, YHR, EKS, and ISP are current employees of Nunaps Inc. DWK is the founder and chief executive officer of Nunaps Inc. and owns stock.
Figures



References
-
- Petersen, R. C. et al. Mild cognitive impairment: Clinical characterization and outcome. Arch Neurol.56, 303–308 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Gauthier, S. et al. Mild cognitive impairment. Lancet367, 1262–1270 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Kasper, S. et al. Management of mild cognitive impairment (MCI): The need for national and international guidelines. World J. Biol. Psychiatr.21, 579–594 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

