Distinct mechanisms control the specific synaptic functions of Neuroligin 1 and Neuroligin 2
- PMID: 39747663
- PMCID: PMC11811269
- DOI: 10.1038/s44319-024-00286-4
Distinct mechanisms control the specific synaptic functions of Neuroligin 1 and Neuroligin 2
Abstract
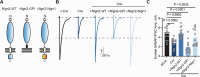
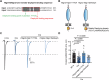
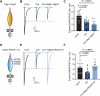
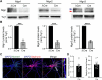
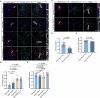
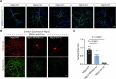
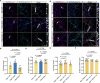
Neuroligins are postsynaptic cell-adhesion molecules that regulate synaptic function with a remarkable isoform specificity. Although Nlgn1 and Nlgn2 are highly homologous and biochemically interact with the same extra- and intracellular proteins, Nlgn1 selectively functions in excitatory synapses whereas Nlgn2 functions in inhibitory synapses. How this excitatory/inhibitory (E/I) specificity arises is unknown. Using a comprehensive structure-function analysis, we here expressed wild-type and mutant neuroligins in functional rescue experiments in cultured hippocampal neurons lacking all endogenous neuroligins. Electrophysiology confirmed that Nlgn1 and Nlgn2 selectively restored excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmission, respectively, in neuroligin-deficient neurons, aligned with their synaptic localizations. Chimeric Nlgn1-Nlgn2 constructs reveal that the extracellular neuroligin domains confer synapse specificity, whereas their intracellular sequences are exchangeable. However, the cytoplasmic sequences of Nlgn2, including its Gephyrin-binding motif that is identically present in the Nlgn1, is essential for its synaptic function whereas they are dispensable for Nlgn1. These results demonstrate that although the excitatory vs. inhibitory synapse specificity of Nlgn1 and Nlgn2 are both determined by their extracellular sequences, these neuroligins enable normal synaptic connections via distinct intracellular mechanisms.
Keywords: Distinct Mechanisms; Extracellular Domain; Intracellular Domain; Neuroligin; Synapse Specific.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

