A phosphate-binding pocket in cyclin B3 is essential for XErp1/Emi2 degradation in meiosis I
- PMID: 39747666
- PMCID: PMC11811201
- DOI: 10.1038/s44319-024-00347-8
A phosphate-binding pocket in cyclin B3 is essential for XErp1/Emi2 degradation in meiosis I
Abstract
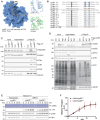
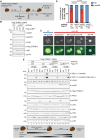
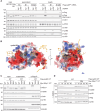
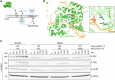
To ensure the correct euploid state of embryos, it is essential that vertebrate oocytes await fertilization arrested at metaphase of meiosis II. This MII arrest is mediated by XErp1/Emi2, which inhibits the ubiquitin ligase APC/C (anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome). Cyclin B3 in complex with Cdk1 (cyclin-dependent kinase 1) is essential to prevent an untimely arrest of vertebrate oocytes in meiosis I by targeting XErp1/Emi2 for degradation. Yet, the molecular mechanism of XErp1/Emi2 degradation in MI is not well understood. Here, by combining TRIM-Away in oocytes with egg extract and in vitro studies, we demonstrate that a hitherto unknown phosphate-binding pocket in cyclin B3 is essential for efficient XErp1/Emi2 degradation in meiosis I. This pocket enables Cdk1/cyclin B3 to bind pre-phosphorylated XErp1/Emi2 facilitating further phosphorylation events, which ultimately target XErp1/Emi2 for degradation in a Plk1- (Polo-like kinase 1) dependent manner. Key elements of this degradative mechanism are conserved in frog and mouse. Our studies identify a novel, evolutionarily conserved determinant of Cdk/cyclin substrate specificity essential to prevent an untimely oocyte arrest at meiosis I with catastrophic consequences upon fertilization.
Keywords: APC/C; Cyclin B3; Emi2; Phosphate-binding Pocket; XErp1.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

