Phytochemical fingerprinting of phytotoxins as a cutting-edge approach for unveiling nature's secrets in forensic science
- PMID: 39747712
- PMCID: PMC11695570
- DOI: 10.1007/s13659-024-00484-6
Phytochemical fingerprinting of phytotoxins as a cutting-edge approach for unveiling nature's secrets in forensic science
Abstract
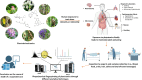
The integration of phytochemistry into forensic science has emerged as a groundbreaking frontier, providing unprecedented insights into nature's secrets through the precise application of phytochemical fingerprinting of phytotoxins as a cutting-edge approach. This study explores the dynamic intersection of phytochemistry and forensic science, highlighting how the unique phytochemical profiles of toxic plants and their secondary metabolites, serve as distinctive markers for forensic investigations. By utilizing advanced techniques such as Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UHPLC) and High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (HRMS), the detection and quantification of plant-derived are made more accurate in forensic contexts. Real-world case studies are presented to demonstrate the critical role of plant toxins in forensic outcomes and legal proceedings. The challenges, potential, and future prospects of integrating phytochemical fingerprinting of plant toxins into forensic science were discussed. This review aims to illuminate phytochemical fingerprinting of plant toxins as a promising tool to enhance the precision and depth of forensic analyses, offering new insights into the complex stories embedded in plant toxins.
Keywords: Advanced chromatography; Forensic phytochemistry; Phytochemical fingerprinting; Plant toxins.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. The authors declare that they have no competing of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Coyle HM. Forensic botany: principles and applications to criminal casework. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2004.
-
- Hall DW, Byrd J. Forensic botany: a practical guide. Boca Raton: John Wiley & Sons; 2012.
-
- Bock JH, Norris DO. Forensic plant science. Amsterdam: Academic Press; 2015.
-
- Coyle HM, Lee C-L, Lin W-Y, Lee HC, Palmbach TM. Forensic botany: using plant evidence to aid in forensic death investigation. Croat Med J. 2005;46(4):606. - PubMed
-
- Coyle HM, Ladd C, Palmbach T, Lee HC. The green revolution: botanical contributions to forensics and drug enforcement. Croat Med J. 2001;42:340–5. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

