The role of artificial intelligence in pandemic responses: from epidemiological modeling to vaccine development
- PMID: 39747786
- PMCID: PMC11695538
- DOI: 10.1186/s43556-024-00238-3
The role of artificial intelligence in pandemic responses: from epidemiological modeling to vaccine development
Abstract
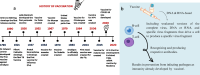
Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) across numerous disciplines has transformed the worldwide landscape of pandemic response. This review investigates the multidimensional role of AI in the pandemic, which arises as a global health crisis, and its role in preparedness and responses, ranging from enhanced epidemiological modelling to the acceleration of vaccine development. The confluence of AI technologies has guided us in a new era of data-driven decision-making, revolutionizing our ability to anticipate, mitigate, and treat infectious illnesses. The review begins by discussing the impact of a pandemic on emerging countries worldwide, elaborating on the critical significance of AI in epidemiological modelling, bringing data-driven decision-making, and enabling forecasting, mitigation and response to the pandemic. In epidemiology, AI-driven epidemiological models like SIR (Susceptible-Infectious-Recovered) and SIS (Susceptible-Infectious-Susceptible) are applied to predict the spread of disease, preventing outbreaks and optimising vaccine distribution. The review also demonstrates how Machine Learning (ML) algorithms and predictive analytics improve our knowledge of disease propagation patterns. The collaborative aspect of AI in vaccine discovery and clinical trials of various vaccines is emphasised, focusing on constructing AI-powered surveillance networks. Conclusively, the review presents a comprehensive assessment of how AI impacts epidemiological modelling, builds AI-enabled dynamic models by collaborating ML and Deep Learning (DL) techniques, and develops and implements vaccines and clinical trials. The review also focuses on screening, forecasting, contact tracing and monitoring the virus-causing pandemic. It advocates for sustained research, real-world implications, ethical application and strategic integration of AI technologies to strengthen our collective ability to face and alleviate the effects of global health issues.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; COVID-19; Epidemiological modelling; Global health; Machine learning algorithms; SARS-CoV-2; Vaccine development.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
