π-PrimeNovo: an accurate and efficient non-autoregressive deep learning model for de novo peptide sequencing
- PMID: 39747823
- PMCID: PMC11695716
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55021-3
π-PrimeNovo: an accurate and efficient non-autoregressive deep learning model for de novo peptide sequencing
Abstract
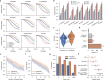
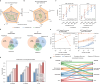
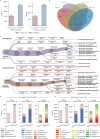
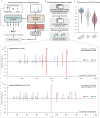
Peptide sequencing via tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) is essential in proteomics. Unlike traditional database searches, deep learning excels at de novo peptide sequencing, even for peptides missing from existing databases. Current deep learning models often rely on autoregressive generation, which suffers from error accumulation and slow inference speeds. In this work, we introduce π-PrimeNovo, a non-autoregressive Transformer-based model for peptide sequencing. With our architecture design and a CUDA-enhanced decoding module for precise mass control, π-PrimeNovo achieves significantly higher accuracy and up to 89x faster inference than state-of-the-art methods, making it ideal for large-scale applications like metaproteomics. Additionally, it excels in phosphopeptide mining and detecting low-abundance post-translational modifications (PTMs), marking a substantial advance in peptide sequencing with broad potential in biological research.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evaluating de novo sequencing in proteomics: already an accurate alternative to database-driven peptide identification?Brief Bioinform. 2018 Sep 28;19(5):954-970. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbx033. Brief Bioinform. 2018. PMID: 28369237
-
Computational Methods in Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;939:63-89. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-1503-8_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27807744 Review.
-
NovoRank: Refinement for De Novo Peptide Sequencing Based on Spectral Clustering and Deep Learning.J Proteome Res. 2025 Feb 7;24(2):903-910. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.4c00300. Epub 2024 Dec 31. J Proteome Res. 2025. PMID: 39739539
-
De novo sequencing with limited number of post-translational modifications per peptide.J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2013 Aug;11(4):1350007. doi: 10.1142/S0219720013500078. Epub 2013 Apr 11. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2013. PMID: 23859271
-
Algorithms for the de novo sequencing of peptides from tandem mass spectra.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2011 Oct;8(5):645-57. doi: 10.1586/epr.11.54. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2011. PMID: 21999834 Review.
References
-
- Aebersold, R. & Mann, M. Mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Nature422, 198–207 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Cox, J. & Mann, M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p. Nat. Biotechnol.26, 1367–1372 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Eng, J. K., McCormack, A. L. & Yates, J. R. An approach to correlate tandem mass spectral data of peptides with amino acid sequences in a protein database. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom.5, 976–989 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Perkins, D. N., Pappin, D. J., Creasy, D. M. & Cottrell, J. S. Probability-based protein identification by searching sequence databases using mass spectrometry data. Electrophoresis20, 3551–3567 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

