Radiopharmaceuticals and their applications in medicine
- PMID: 39747850
- PMCID: PMC11697352
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-024-02041-6
Radiopharmaceuticals and their applications in medicine
Abstract
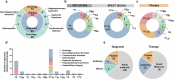
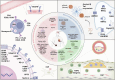
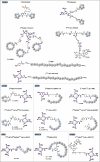
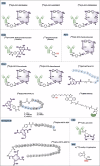
Radiopharmaceuticals involve the local delivery of radionuclides to targeted lesions for the diagnosis and treatment of multiple diseases. Radiopharmaceutical therapy, which directly causes systematic and irreparable damage to targeted cells, has attracted increasing attention in the treatment of refractory diseases that are not sensitive to current therapies. As the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approvals of [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-TATE, [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 and their complementary diagnostic agents, namely, [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TATE and [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11, targeted radiopharmaceutical-based theranostics (radiotheranostics) are being increasingly implemented in clinical practice in oncology, which lead to a new era of radiopharmaceuticals. The new generation of radiopharmaceuticals utilizes a targeting vector to achieve the accurate delivery of radionuclides to lesions and avoid off-target deposition, making it possible to improve the efficiency and biosafety of tumour diagnosis and therapy. Numerous studies have focused on developing novel radiopharmaceuticals targeting a broader range of disease targets, demonstrating remarkable in vivo performance. These include high tumor uptake, prolonged retention time, and favorable pharmacokinetic properties that align with clinical standards. While radiotheranostics have been widely applied in tumor diagnosis and therapy, their applications are now expanding to neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and inflammation. Furthermore, radiotheranostic-empowered precision medicine is revolutionizing the cancer treatment paradigm. Diagnostic radiopharmaceuticals play a pivotal role in patient stratification and treatment planning, leading to improved therapeutic outcomes in targeted radionuclide therapy. This review offers a comprehensive overview of the evolution of radiopharmaceuticals, including both FDA-approved and clinically investigated agents, and explores the mechanisms of cell death induced by radiopharmaceuticals. It emphasizes the significance and future prospects of theranostic-based radiopharmaceuticals in advancing precision medicine.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



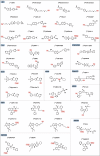
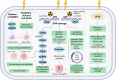
References
-
- Bollineni, V. R., Collette, S. & Liu, Y. Functional and molecular imaging in cancer drug development. Chin. Clin. Oncol.3, 17 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

