Artificial molecular communication network based on DNA nanostructures recognition
- PMID: 39747880
- PMCID: PMC11696045
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55527-w
Artificial molecular communication network based on DNA nanostructures recognition
Abstract
Artificial simulated communication networks inspired by molecular communication in organisms use biological and chemical molecules as information carriers to realize information transmission. However, the design of programmable, multiplexed and general simulation models remains challenging. Here, we develop a DNA nanostructure recognition-based artificial molecular communication network (DR-AMCN), in which rectangular DNA origami nanostructures serve as nodes and their recognition as edges. After the implementation of DR-AMCN with various communication mechanisms including serial, parallel, orthogonal, and multiplexing, it is applied to construct various communication network topologies with bus, ring, star, tree, and hybrid structures. By the establishment of a node partition algorithm for path traversal based on DR-AMCN, the computational complexity of the seven-node Hamiltonian path problem is reduced with the final solution directly obtained through the rate-zonal centrifugation method, and scalability of this approach is also demonstrated. The developed DR-AMCN enhances our understanding of signal transduction mechanisms, dynamic processes, and regulatory networks in organisms, contributing to the solution of informatics and computational problems, as well as having potential in computer science, biomedical engineering, information technology and other related fields.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
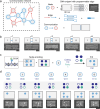



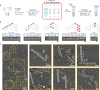

References
-
- El-atty, Abd et al. Engineering molecular communications integrated with carbon nanotubes in neural sensor nanonetworks. IET Nanobiotechnol.12, 201–210 (2018). - DOI
-
- Nakano, T. et al. Performance evaluation of leader-follower-based mobile molecular communication networks for target detection applications. IEEE Trans. Commun.65, 663–676 (2017). - DOI
-
- Bayraktar, Y. et al. Analyzing of alzheimer’s disease based on biomedical and socio-economic approach using molecular communication, artificial neural network, and random forest models. Sustainability14, 7901 (2022). - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

