A pre-clinical MRI-guided all-in-one focused ultrasound system for murine brain studies
- PMID: 39747938
- PMCID: PMC11696467
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-84078-9
A pre-clinical MRI-guided all-in-one focused ultrasound system for murine brain studies
Abstract
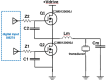
This paper describes the design and initial proof-of-concept of a single pre-clinical transcranial focused ultrasound (FUS) system capable of performing histotripsy (mechanical ablation), hyperthermia, blood-brain barrier opening (BBBO), sonodynamic therapy, or neuromodulation in a murine brain. We have termed it the All-in-One FUS system for murine brain studies, which is the first FUS system of its kind. The 1.5 MHz ultrasound transducer was fabricated and driven using a custom electronic driver to produce 3-cycle pulses with a focal peak-negative pressure (P-) of up to 87 MPa at a low duty cycle (< 0.1%) for histotripsy as well as 50% duty cycle pulsed-ultrasound with a spatial-peak temporal-average intensity (Ispta) of up to 251 W/cm2 for the other FUS modalities. This All-in-One system can be guided by MRI or stereotactically to maximize its flexibility. To validate the design of the system, histotripsy, BBBO, and hyperthermia were performed in naïve brains of two mice for each modality. Histotripsy and BBBO were performed using MRI-based stereotactic co-registration. The therapeutic effect was confirmed using T2-weighted MR-images for histotripsy, and T1-weighted Gadolinium contrast-enhanced MR-images for BBBO. For hyperthermia, an MRI-compatible insert was designed to fit inside the 80 mm imaging coil of a 7-Tesla small-animal MRI-system, with T2-weighted MR-images used to confirm targeting, and MR-thermometry used to monitor the thermal dose delivered.
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier opening; Brain; Histotripsy; Hyperthermia; Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); Therapeutic ultrasound.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Drs. Jonathan Sukovich, Zhen Xu, Timothy L. Hall, and University of Michigan have conflict of interests with HistoSonics. The remaining authors do not any conflicts of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Characterization of Blood-Brain Barrier Opening Induced by Transcranial Histotripsy in Murine Brains.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2024 May;50(5):639-646. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2023.12.014. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38302370 Free PMC article.
-
Transcranial MRI-guided Histotripsy Targeting Using MR-thermometry and MR-ARFI.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2025 Feb;51(2):330-335. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2024.10.010. Epub 2024 Nov 25. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 39592380
-
Magnetic Resonance Thermometry Targeting for Magnetic Resonance-Guided Histotripsy Treatments.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2023 May;49(5):1102-1107. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2022.12.009. Epub 2023 Feb 19. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 36801181 Free PMC article.
-
Revolutionizing brain interventions: the multifaceted potential of histotripsy.Neurosurg Rev. 2024 Mar 21;47(1):124. doi: 10.1007/s10143-024-02353-9. Neurosurg Rev. 2024. PMID: 38509320 Review.
-
Overcoming the Blood-Brain Barrier: Focused Ultrasound in Glioblastoma Treatment.Cureus. 2025 Apr 23;17(4):e82869. doi: 10.7759/cureus.82869. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40416199 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gerhardson, T. Transcranial Therapy for Intracerebral Hemorrhage and Other Brain Pathologies using Histotripsy (2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

