Neurotensin-neurotensin receptor 2 signaling in adipocytes suppresses food intake through regulating ceramide metabolism
- PMID: 39748047
- PMCID: PMC11770130
- DOI: 10.1038/s41422-024-01038-8
Neurotensin-neurotensin receptor 2 signaling in adipocytes suppresses food intake through regulating ceramide metabolism
Abstract
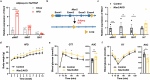
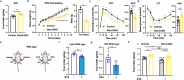
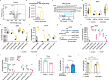
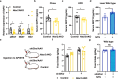
Neurotensin (NTS) is a secretory peptide produced by lymphatic endothelial cells. Our previous study revealed that NTS suppressed the activity of brown adipose tissue via interactions with NTSR2. In the current study, we found that the depletion of Ntsr2 in white adipocytes upregulated food intake, while the local treatment of NTS suppressed food intake. Our mechanistic study revealed that suppression of NTS-NTSR2 signaling enhanced the phosphorylation of ceramide synthetase 2, increased the abundance of its products ceramides C20-C24, and downregulated the production of GDF15 in white adipose tissues, which was responsible for the elevation of food intake. We discovered a potential causal and positive correlation between serum C20-C24 ceramide levels and human food intake in four populations with different ages and ethnic backgrounds. Together, our study shows that NTS-NTSR2 signaling in white adipocytes can regulate food intake via its direct control of lipid metabolism and production of GDF15. The ceramides C20-C24 are key factors regulating food intake in mammals.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Halaas, J. L. et al. Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. Science269, 543–546 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Kershaw, E. E. & Flier, J. S. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.89, 2548–2556 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Lin, Y. et al. The chemerin-CMKLR1 axis limits thermogenesis by controlling a beige adipocyte/IL-33/type 2 innate immunity circuit. Sci. Immunol.6, eabg9698 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Checler, F., Barelli, H., Kitabgi, P. & Vincent, J. P. Neurotensin metabolism in various tissues of central and peripheral origins: ubiquitous involvement of a novel neurotensin degrading metalloendopeptidase. Biochimie70, 75–82 (1988). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

