Evaluation of long-acting cabotegravir safety and pharmacokinetics in pregnant women in eastern and southern Africa: a secondary analysis of HPTN 084
- PMID: 39748218
- PMCID: PMC11695207
- DOI: 10.1002/jia2.26401
Evaluation of long-acting cabotegravir safety and pharmacokinetics in pregnant women in eastern and southern Africa: a secondary analysis of HPTN 084
Abstract
Introduction: Long-acting injectable cabotegravir (CAB-LA) for pre-exposure prophylaxis significantly reduced HIV acquisition in HPTN 084. We report on the safety and CAB-LA pharmacokinetics in pregnant women during the blinded period of HPTN 084.
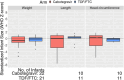
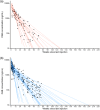
Methods: Participants were randomized 1:1 to either active cabotegravir (CAB) plus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine (TDF/FTC) placebo or active TDF/FTC plus CAB placebo. Pregnancy testing was performed at each visit; participants with a positive test had study product withheld and were offered open-label TDF/FTC. Pregnancies were confirmed on two tests at least 4 weeks apart. All participants with a positive pregnancy test prior to November 5, 2020 are included in this analysis. Pregnancy incidence, maternal adverse event (AE) incidence, pregnancy outcomes (including composite outcome of spontaneous abortion <20 weeks, intrauterine foetal death or stillbirth ≥20 weeks, premature birth <37 weeks, or small for gestational age) were assessed. The apparent terminal phase half-life (t1/2app) of CAB-LA in pregnant women in HPTN 084 was compared to non-pregnant women from the phase 2a HPTN 077 trial. Multivariable models assessed associations with t1/2app. RESULTS: Fifty-seven pregnancies (30 CAB-LA, 27 TDF/FTC) were confirmed over 3845 person-years [py] (incidence 1.5/100 py, 95% CI 1.1-1.9). CAB-LA group participants had a median 342 days (IQR 192, 497) of CAB-LA exposure prior to pregnancy detection. Grade 2 or higher maternal AE incidence did not differ by study arm (CAB 157, 95% CI 91-271 per 100 py vs. TDF/FTC 217, 95% CI 124-380 per 100 py; p = 0.256). Most pregnancies (81%) resulted in live births (25 CAB-LA, 22 TDF/FTC). Composite poor pregnancy outcomes did not differ significantly by group (CAB 6/30 vs. TDF/FTC 4/27; p = 0.476). No congenital anomalies were observed. The CAB t1/2app geometric mean was 52.8 days (95% CI 40.7-68.4) in pregnant women compared to 60.3 days (95% CI 47.7-76.3; p = 0.66) in non-pregnant women; neither pregnancy nor body mass index were significantly associated with t1/2app.
Conclusions: CAB-LA concentrations post-cessation of injections were generally well tolerated in pregnant women. The t1/2app was comparable between pregnant and non-pregnant women. Ongoing studies will examine the safety and pharmacology of CAB-LA in women who choose to continue CAB-LA through pregnancy and lactation.
Keywords: HIV prevention; PrEP; cabotegravir; long‐acting; pregnancy; women.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of the International AIDS Society published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the International AIDS Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare, except SLF and ARR who are paid employees of ViiV Healthcare, and JR who is a paid employee of Gilead Sciences.
Figures

References
-
- UNAIDS . Women and girls carry the heaviest HIV burden in sub‐Saharan Africa. 2022. (accessed 23/03/2024). https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/presscentre/featurestories/2022/marc...
-
- Bongaarts J. Trends in fertility and fertility preferences in sub‐Saharan Africa: the roles of education and family planning programs. Genus. 2020;76(1):32.
-
- ViiV Healthcare . Cabotegravir Investigator's Brochure. version 14 ed. Durham, NC: ViiV Healthcare; 2024.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UM1AI068613/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069424/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
- UM1 AI069530/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- ViiV Healthcare
- UM1 AI068613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI154468/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069436/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068617/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1AI068619/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069530/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- NH/NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068619/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1AI068617/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- OPP1154174/GATES/Gates Foundation/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

