Characterization and Analytical Method Validation for Potential Impurities of a Merchantability Drug Substance Fluoxetine HCl
- PMID: 39748240
- PMCID: PMC11695798
- DOI: 10.1002/bmc.6069
Characterization and Analytical Method Validation for Potential Impurities of a Merchantability Drug Substance Fluoxetine HCl
Abstract
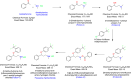
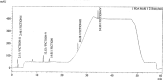
A new selective and sensitive high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method was developed for the quantification of potential impurities in fluoxetine hydrochloride. Chromatographic separation was achieved on an end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel (Gemini-C18 150 mm × 4.6 mm, 3.0 μm) using a gradient program with triethylamine, methanol, and water as the mobile phase at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min and monitored at 215 nm. The run time was 60 min. The method was validated to fulfill International Conference on Harmonization (ICH Q2(R2)) requirements, and this validation included specificity, precision, linearity, limit of detection (LOD), limit of quantification (LOQ), and accuracy. The calibration curve was linear over the concentration range from LOQ to 120% with respect to sample concentration. The accuracy of the method is within the acceptable limit of 80%-120%. The results obtained for all parameters were within the acceptance criteria. So, this method can be employed for the regular analysis of potential impurities in the fluoxetine hydrochloride API.
Keywords: fluoxetine hydrochloride; method validation; nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy; reverse phase HPLC.
© 2025 The Author(s). Biomedical Chromatography published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
UPLC and LC-MS studies on degradation behavior of irinotecan hydrochloride and development of a validated stability-indicating ultra-performance liquid chromatographic method for determination of irinotecan hydrochloride and its impurities in pharmaceutical dosage forms.J Chromatogr Sci. 2012 Oct;50(9):810-9. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/bms075. Epub 2012 Jun 1. J Chromatogr Sci. 2012. PMID: 22661461
-
A Selective and Sensitive Method Development and Validation for Impurity Quantification in Cysteamine Bitartrate Bulk and Formulation by RP-HPLC.Biomed Chromatogr. 2025 Mar;39(3):e70007. doi: 10.1002/bmc.70007. Biomed Chromatogr. 2025. PMID: 39921330
-
Development and validation of a selective, sensitive and stability indicating UPLC-MS/MS method for rapid, simultaneous determination of six process related impurities in darunavir drug substance.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016 Sep 5;128:141-148. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2016.05.026. Epub 2016 May 18. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016. PMID: 27262107
-
Impurity assessment, development and validation of an RP-HPLC method for the determination of eleven potential impurities of eltrombopag precursor.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2024 Jun 15;243:116085. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2024.116085. Epub 2024 Mar 6. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2024. PMID: 38471254 Review.
-
Forced degradation and impurity profiling: recent trends in analytical perspectives.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013 Dec;86:11-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.07.013. Epub 2013 Jul 31. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013. PMID: 23969330 Review.
References
-
- American Society of Health‐System Pharmacists . 2015. Fluoxetine Hydrochloride. Archived From the Original on December 8, 2015.
-
- Ashby, J. , and Tennant R. W.. 1988. “Chemical Structure, Salmonella Mutagenicity and Extent of Carcinogenicity as Indicators of Genotoxic Carcinogenesis Among 222 Chemicals Tested in Rodents by the US NCI/NTP.” Mutation Research, Genetic Toxicology 204, no. 1: 17–115. 10.1016/0165-1218(88)90114-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Clementina, C. I. , Alexandra N. F., and Valentina U.. 2018. “Determination of Fluoxetine Hydrochloride via Ion Pair Complexation With Alizarin Red S.” Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica‐Drug Research 75, no. 6: 1293–1303. 10.32383/appdr/89922. - DOI
-
- Dobo, K. L. , Greene N., Cyr M. O., Caron S., and Ku W. W.. 2006. “The Application of Structure‐Based Assessment to Support Safety and Chemistry Diligence to Manage Genotoxic Impurities in Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients During Drug Development.” Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 44, no. 3: 282–293. 10.1016/j.yrtph.2006.01.004. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources