Association between the triglyceride-glucose index and liver fibrosis in adults with metabolism-related fatty liver disease in the United States: a cross-sectional study of NHANES 2017-2020
- PMID: 39748306
- PMCID: PMC11697960
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-024-03579-z
Association between the triglyceride-glucose index and liver fibrosis in adults with metabolism-related fatty liver disease in the United States: a cross-sectional study of NHANES 2017-2020
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to examine the association between the triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index and liver fibrosis (LF) in U.S. adults with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MAFLD).
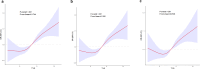
Methods: Using data from the 2017 to 2020 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database, we conducted a population-based cross-sectional study with 1,324 participants. MAFLD was defined as a controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) score ≥ 248 dB/m accompanied by metabolic dysfunction. A median liver stiffness measurement ≥ 8.2 kPa was used to identify significant fibrosis (≥ F2). Multivariable logistic regression was employed to assess the impact of the TyG index on LF outcomes. A restricted cubic spline (RCS) model was used to explore nonlinear effects, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were applied to evaluate the effectiveness in predicting.
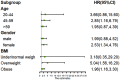
Results: Among the participants, 716 were men and 608 were women, aged 20 to 80 years, representing various racial groups. Significant fibrosis was observed in 137 out of 1,324 participants. After adjusting for confounding factors, a higher TyG index was significantly associated with an increased incidence of MAFLD-related LF (OR = 2.18, 95% CI, 1.14-4.18; p < 0.05). Elevated TyG levels showed a positive correlation with significant fibrosis, with an odds ratio (OR) exceeding 1 when the TyG index was above 8.054. Subgroup analyses stratified by sex, age, and body mass index (BMI) revealed differences after adjusting for confounders. The association was stronger in women (OR = 2.53, 95% CI, 1.16-5.53) than in men (OR = 1.95, 95% CI, 0.81-4.72). A significant correlation was also found between TyG levels and obesity status (overweight: OR = 4.80, 95% CI, 1.27-18.2; obese: OR = 2.26, 95% CI, 1.20-5.53). In MAFLD patients aged 40-59, TyG was strongly associated with LF (OR = 2.85, 95% CI, 1.16-6.79). Furthermore, the area under the ROC curve (AUC) for the TyG index in predicting significant fibrosis in MAFLD patients was 0.73 (95% CI, 0.68-0.78), indicating moderate predictive ability.
Conclusions: In the general U.S. population, elevated TyG index levels were positively associated with an increased risk of LF in MAFLD patients.
Keywords: Liver fibrosis; Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease; NHANES; TyG index.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study involved secondary data analysis of NHANES and was exempt from institutional review. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NO. GZY-ZJ-KJ-23007/State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Department-Zhejiang Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Co-construction of Traditional Chinese Medicine Modernization Research Program Major Project
- NO. GZY-ZJ-SY-2402/State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Department-Zhejiang Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Co-construction of Key Laboratory of Research on Prevention and Treatment for depression syndrome
- 2021]No.40/Zhejiang Province 551 Health Talent Training Project (Zhejiang Provincial Health Commission Office
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous