Effects of physical activity on sleep quality among university students: chain mediation between rumination and depression levels
- PMID: 39748322
- PMCID: PMC11697847
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-024-06450-3
Effects of physical activity on sleep quality among university students: chain mediation between rumination and depression levels
Abstract
Background: Colleges and universities are currently facing the major public health issue of poor sleep quality. Sleep quality must be taken seriously to maintain the students' emotional and physical well-being. Thus, this study sought to determine how university students' levels of physical activity related to the quality of their sleep, as well as to explore the mechanisms via which physical activity affects sleep and provide suggestions for improving it.
Methods: A total of 883 university students from Ganzhou City, Jiangxi Province, China participated in the study. Their physical activity, sleep quality, ruminative thinking levels, and depression were assessed using various questionnaires.
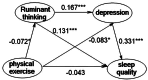
Results: Through the mediating effects of rumination and depression as well as the chain-mediated effects of these two factors, physical exercise changed the quality of sleep.
Conclusion: University students' sleep quality can be improved by increasing their physical activity and decreasing ruminative thinking and depression levels.
Keywords: Mediating effects; Physical activity; Sleep quality; University students.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was conducted in accordance with the Tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. Complete research objectives and survey contents were explained to the participants. All participants provided written informed consent and agreed to the required measurement and survey completion procedures. This study was approved by the Ethical Committee of Gannan Medical University, China, No: 2021110. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Naderi H, Dehghan H, Dehrouyeh S, Tajik E. Academic burnout among undergraduate nursing students: Predicting the role of sleep quality and healthy lifestyle. Res Dev Med Educ. 2021;10(1):16–16. 10.34172/rdme.2021.016. - DOI
-
- Marvaldi M, Mallet J, Dubertret C, Moro MR, Guessoum SB. Anxiety, depression, trauma-related, and sleep disorders among healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021;126:252–64. 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.03.024. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Guo SR. The effect of sleep quality on suicidal ideation in college students: the role of depression and self-esteem. Psychol Res. 2021;14:464–72.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical