Increasing the biomolecular relevance of cell culture practice
- PMID: 39748368
- PMCID: PMC11697962
- DOI: 10.1186/s12929-024-01095-6
Increasing the biomolecular relevance of cell culture practice
Abstract
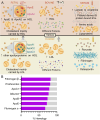
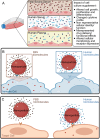
The biomolecular relevance of medium supplements is a key challenge affecting cell culture practice. The biomolecular composition of commonly used supplements differs from that of a physiological environment, affecting the validity of conclusions drawn from in vitro studies. This article discusses the advantages and disadvantages of common supplements, including context-dependent considerations for supplement selection to improve biomolecular relevance, especially in nanomedicine and extracellular vesicle research.
Keywords: Chemically defined medium; Fetal bovine serum (FBS); Plasma; Serum; Supplement.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Sivakumar Joghi Thatha, G. New insights into cell culture technology. (IntechOpen, 2017). 10.5772/62590.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

