Evaluating hospital performance with additive DEA and MPI: the Isfahan University of Medical Science case study
- PMID: 39748389
- PMCID: PMC11694360
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-024-12145-y
Evaluating hospital performance with additive DEA and MPI: the Isfahan University of Medical Science case study
Abstract
Background: Hospitals are a vital pillar of the health system, and measuring their performance by an appropriate quantitative model is crucial. This study evaluated the performance of hospitals affiliated with Isfahan University of Medical Sciences. It deals with the nature of dynamics (the performance of evaluation indicators over time), examining controllable, uncontrollable, and undesirable input and output indicators.
Methods: This study evaluated the performance of 26 Isfahan University of Medical Science hospitals in terms of efficiency and productivity with hybrid Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) models, namely, the additive classic, Malmquist productivity index (MPI), and super-efficiency models, from 2019 through 2022. Thirteen indicators (four inputs and nine outputs) were selected as model variables by brainstorming in the expert panel.
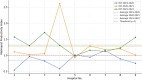
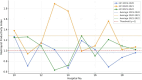
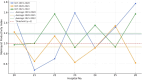
Results: The average technical efficiency of hospitals during the four periods was 0.86, indicating an average inefficiency of 14%. Malmquist productivity index results over four periods showed hospitals operating with an average of 11% positive growth, reflecting an overall increase in productivity. Notably, some hospitals with high technical efficiency displayed lower total productivity growth rates due to fluctuations in specific indicators. On average, in the four under study years, 12 hospitals were efficient, of which 75% (9 hospitals) had performance progress (average MPI > 1). On the contrary, among the 14 inefficient hospitals during the four studied years, more than 90% of the hospitals had improved performance.
Conclusion: This study introduces a multidimensional and dynamic model for evaluating hospital performance. While classic DEA models provide a statistical performance evaluation, the Malmquist Productivity Index reveals dynamic performance changes over time. These findings underscore the need for hospitals to adopt advanced quantitative models to optimize resource allocation and enhance service delivery.
Keywords: Additive DEA model; Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA); Efficiency; Hospital; Malmquist productivity index (MPI); Performance evaluation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kou R, Mei K, Bi Y, Huang J, Yang S, Chen K, et al. Efficiency and equity of hospital services in mainland China: based on data from 2017 to 2021. 2023.
-
- Hadji B, Degoulet P. Measuring hospital technical efficiency with data envelopment analysis, application to 20 Paris public university hospitals. 2023.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources