Integrative analyses of mendelian randomization and bioinformatics reveal casual relationship and genetic links between COVID-19 and knee osteoarthritis
- PMID: 39748395
- PMCID: PMC11697936
- DOI: 10.1186/s12920-024-02074-4
Integrative analyses of mendelian randomization and bioinformatics reveal casual relationship and genetic links between COVID-19 and knee osteoarthritis
Abstract
Background: Clinical and epidemiological analyses have found an association between coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and knee osteoarthritis (KOA). Infection with COVID-19 may increase the risk of developing KOA.
Objectives: This study aimed to investigate the potential causal relationship between COVID-19 and KOA using Mendelian randomization (MR) and to explore the underlying mechanisms through a systematic bioinformatics approach.
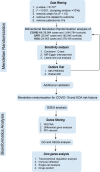
Methods: Our investigation focused on exploring the potential causal relationship between COVID-19, acute upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) and KOA utilizing a bidirectional MR approach. Additionally, we conducted differential gene expression analysis using public datasets related to these three conditions. Subsequent analyses, including transcriptional regulation analysis, immune cell infiltration analysis, single-cell analysis, and druggability evaluation, were performed to explore potential mechanisms and prioritize therapeutic targets.
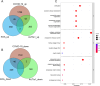
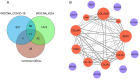
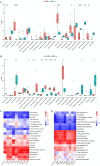
Results: The results indicate that COVID-19 has a one-way impact on KOA, while URTI does not play a causal role in this association. Ribosomal dysfunction may serve as an intermediate factor connecting COVID-19 with KOA. Specifically, COVID-19 has the potential to influence the metabolic processes of the extracellular matrix, potentially impacting the joint homeostasis. A specific group of genes (COL10A1, BGN, COL3A1, COMP, ACAN, THBS2, COL5A1, COL16A1, COL5A2) has been identified as a shared transcriptomic signature in response to KOA with COVID-19. Imatinib, Adiponectin, Myricetin, Tranexamic acid, and Chenodeoxycholic acid are potential drugs for the treatment of KOA patients with COVID-19.
Conclusions: This study uniquely combines Mendelian randomization and bioinformatics tools to explore the possibility of a causal relationship and genetic association between COVID-19 and KOA. These findings are expected to provide novel perspectives on the underlying biological mechanisms that link COVID-19 and KOA.
Keywords: Acute upper respiratory tract infection (URTI); Bioinformatics analysis; COVID-19; Knee osteoarthritis (KOA); Mendelian randomization (MR).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. The data used for analysis were obtained from published studies and public databases, no additional ethics approval was needed. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Causal relationship between sarcopenia with osteoarthritis and the mediating role of obesity: a univariate, multivariate, two-step Mendelian randomization study.BMC Geriatr. 2024 May 29;24(1):469. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-05098-8. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 38811889 Free PMC article.
-
Causal relationship between periodontal disease-related phenotype and knee osteoarthritis: A two-sample mendelian randomization analysis.PLoS One. 2024 May 31;19(5):e0304117. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304117. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38820296 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring causal correlations between inflammatory cytokines and knee osteoarthritis: a two-sample Mendelian randomization.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 18;15:1362012. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1362012. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38698846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral infections of the central nervous system increase the risk of knee osteoarthritis: a two-sample mendelian randomization study.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2025 Jan 21;37(1):30. doi: 10.1007/s40520-025-02927-7. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2025. PMID: 39836329 Free PMC article.
-
A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study of Sarcopenia-Related Traits and Knee Osteoarthritis.Clin Interv Aging. 2023 Sep 15;18:1577-1586. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S424633. eCollection 2023. Clin Interv Aging. 2023. PMID: 37731961 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Injections of Monocytes, Platelet-Rich Plasma, and Hyaluronic Acid in Adults with Knee Osteoarthritis: An Observational Study.J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2025 Mar 26;10(2):104. doi: 10.3390/jfmk10020104. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2025. PMID: 40566402 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huzum B, Curpan AS, Puha B, Serban DN, Veliceasa B, Necoara RM et al. Connections between Orthopedic Conditions and Oxidative Stress: Current Perspective and the Possible Relevance of Other Factors, Such as Metabolic Implications, Antibiotic Resistance, and COVID-19. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022;58(3). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

