Impact of diagnosis-related group payment on medical expenditure and treatment efficiency on people with drug-resistant tuberculosis: a quasi-experimental study design
- PMID: 39748411
- PMCID: PMC11697884
- DOI: 10.1186/s12939-024-02368-0
Impact of diagnosis-related group payment on medical expenditure and treatment efficiency on people with drug-resistant tuberculosis: a quasi-experimental study design
Abstract
Background: The severe health challenge and financial burden of drug-resistant tuberculosis (DR-TB) continues to be an impediment in China and worldwide. This study aimed to explore the impact of Diagnosis-related group (DRG) payment on medical expenditure and treatment efficiency among DR-TB patients.
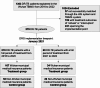
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included all DR-TB patients from the digitized Hospital Information System (HIS) of Wuhan Pulmonary Hospital and the TB Information Management System (TBIMS) with completed full course of National Tuberculosis Program (NTP) standard treatment in Wuhan from January 2016 to December 2022, excluding patients whose treatment spanned both before and after the DRG timepoint. These patients are all receiving standardized treatment specified by the NTP in designated tuberculosis hospitals. We performed the difference-in-differences (DID) model to investigate 6 primary outcomes. The cost-shifting behaviors were also examined using 4 outpatient and out-of-pocket (OOP) indicators. In the DID model, the baseline period is set from January 2016 to December 2020 before the DRG payment reform, while the treatment period is from January 2021 to December 2022. The payment reform only applied to individuals covered by Wuhan Municipal Medical Insurance, so the treatment group consists of patients insured by this plan, with other patients serving as the control group.
Results: In this study, 279 patients were included in the analysis, their average treatment duration was 692.79 days. We found the DRG payment implementation could effectively reduce the total medical expenditure, total inpatient expenditure, and inpatient expenditure per hospitalization by 28636.03RMB (P < 0.01), 22035.03 RMB (P < 0.01) and 2448.00 RMB (P < 0.05). We also found a reduction in inpatient frequency and inpatient length of stays per hospitalization by 1.32 and 2.63 days with significance. The spillover effects of the DRG payment on outpatient and OOP expenditure were statistically insignificant.
Conclusions: The DRG payment method can effectively control the increase of DR-TB patients' medical expenditure and improve treatment efficiency with the guarantee of care quality. Furthermore, there was no evidence of spillover effects of DRG payment on outpatient and out-of-pocket expenditures.
Keywords: Diagnosis-related group (DRG); Difference-in-differences (DID); Drug-resistant tuberculosis (DR-TB); Medical expenditure; Treatment efficiency.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Research involving human data has been performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations in the declaration. The study was approved by the institutional review board at each participating site and by the biomedical ethics review committee of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (S170. June 30, 2021). The need for informed consent was waived by the ethics institutional review board of Huazhong University of Science and Technology because of the retrospective nature of the study. All authors confirm that this research caused no harm (physical or mental) to any participants. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that there were no competing interests.
References
-
- Global tuberculosis report 2023. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2023.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources