Evaluation of pediatric cochlear implantation results
- PMID: 39748690
- PMCID: PMC11770799
- DOI: 10.62438/tunismed.v102i12.4977
Evaluation of pediatric cochlear implantation results
Abstract
Background: Cochlear implantation is an effective method of auditory rehabilitation. Nevertheless, the results show individual variations depending on several factors.
Aim: To evaluate cochlear implantation results based on the APCEI profile (Acceptance, Perception, Comprehension, Oral Expression and Intelligibility) and audiometric results.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study including children under 18 years of age who had a unilateral cochlear implant and whose implants had been activated at least 1 year prior to the start of the study. During this study period, 75 children underwent unilateral cochlear implantation. Among them, 44 patients had reached one year after the activation of the implant at the time of the evaluation and were then included in the analytical part. A speech-language pathology assessment using the APCEI scale was conducted for 44 cases. Thirty-eight cases had an audiometric assessment (free-field tone audiometry and speech audiometry). We assessed the results of the APCEI profile based on various factors.
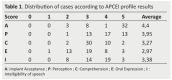
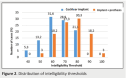
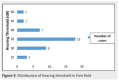
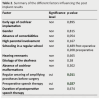
Results: The mean cochlear implantation age was 5 years and 2 months. The electrode insertion was complete in all cases. The APCEI profile average was 3.6. Four children had poor results, 27 children had good results, and 13 children had excellent results. The average hearing threshold in tonal audiometry was 39dB. In voice audiometry, the average intelligibility threshold was 65% with the cochlear implant versus 75% with the cochlear implant and the contra lateral hearing aid. According to the statistical study, only two factors were considered to have a positive influence on the success rate of cochlear implantation: the regular use of preoperative amplificative prostheses and the follow-up of speech therapy sessions in pre-operative.
Conclusion: The effectiveness of cochlear implantation depends on several factors. Multidisciplinary management improves the results.
Keywords: APCEI profile; Child; Cochlear implantation; Deafness; Results.
Figures
References
-
- Vieira S, Dupas G, Chiari BM. Cochlear implant: the family’s perspective. Cochlear Implants Int. 2018;19(4):216–224. - PubMed
-
- Sharma SD, Cushing SL, Papsin BC, Gordon KA. Hearing and speech benefits of cochlear implantation in children: A review of the literature. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2020;133:109984. - PubMed
-
- Kessentini A, Marrakchi J. [Faculté de médecine de Tunis]: Elmanar Tunis. 2019. Implant cochléaire chez l’enfant: Evaluation des résultats par le profil acceptation de l’implant, perception auditive, compréhension orale, expression orale, Intelligibilité vocale.
-
- Chilosi AM, Comparini A, Scusa MF, et al. A Longitudinal Study of Lexical and Grammar Development in Deaf Italian Children Provided With Early Cochlear Implantation. Ear Hear. 2013;34(3):28–37. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical