Self-Esteem and College Students' Online Impulse Buying: The Independent and Interactive Moderating Role of Interdependent Self-Construal and Interpersonal Relationships
- PMID: 39748802
- PMCID: PMC11694021
- DOI: 10.2147/PRBM.S494636
Self-Esteem and College Students' Online Impulse Buying: The Independent and Interactive Moderating Role of Interdependent Self-Construal and Interpersonal Relationships
Abstract
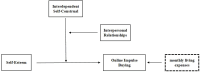
Purpose: Despite the extensive research examining the antecedents and consequences of impulse behavior, empirical studies exploring the role of self-esteem in college students' online impulse buying remain relatively scarce. Drawing on the theory of compensatory consumption, the current study aimed to examine the influence of self-esteem on college students' online impulse buying and the independent and interactive moderating role of interdependent self-construal and interpersonal relationships.
Patients and methods: This study recruited 323 college students through random sampling and invited them to complete self-reported questionnaires measuring self-esteem, online impulse buying, interdependent self-construal, and interpersonal relationships. To test the research hypotheses, SPSS 27.0 was used for reliability analysis, correlation analysis, tests of convergent and discriminant validity, hierarchical linear regression analyses, and simple slope analyses to examine moderation effects.
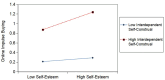
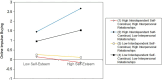
Results: The study found that self-esteem is negatively associated with online impulse buying among college students. More importantly, interdependent self-construal strengthens this negative relationship, with the effect being significantly stronger for students who exhibit higher levels of interdependent self-construal. Furthermore, a three-way interaction revealed that the inhibitory effect of self-esteem on online impulse buying is strongest when students have both high interdependent self-construal and low-quality interpersonal relationships, compared to other combinations of these factors.
Conclusion: This study enhances our understanding of the relationship between self-esteem and online impulse buying by examining the moderating effects of interdependent self-construal and interpersonal relationships. Specifically, the inhibitory effect of self-esteem on online impulse buying is strongest among college students with low-quality interpersonal relationships and a high level of interdependent self-construal. These findings explore how interpersonal factors shape the relationship between self-esteem and online impulse buying, offering practical guidance for preventing and intervening in online impulse buying among college students.
Keywords: college students; interdependent self-construal; interpersonal relationships; online impulse buying; self-esteem.
© 2024 Guo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Chan TKH, Cheung CMK, Lee ZWY. The state of online impulse-buying research: a literature analysis. Inform Manage. 2017;54(2):204–217. doi: 10.1016/j.im.2016.06.001 - DOI
-
- Rook DW. The buying impulse. J Consum Res. 1987;14(2):189–199. doi: 10.1086/209105 - DOI
-
- Pereira ML, de La Martinière Petroll M, Soares JC, CAd M, Hernani-Merino M. Impulse buying behaviour in omnichannel retail: an approach through the stimulus-organism-response theory. Int J Retail Distrib. 2023;51(1):39–58. doi: 10.1108/IJRDM-09-2021-0394 - DOI
-
- Beatty SE, Ferrell ME. Impulse buying: modeling its precursors. J Retailing. 1998;74(2):169–191. doi: 10.1016/S0022-4359(99)80092-X - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources